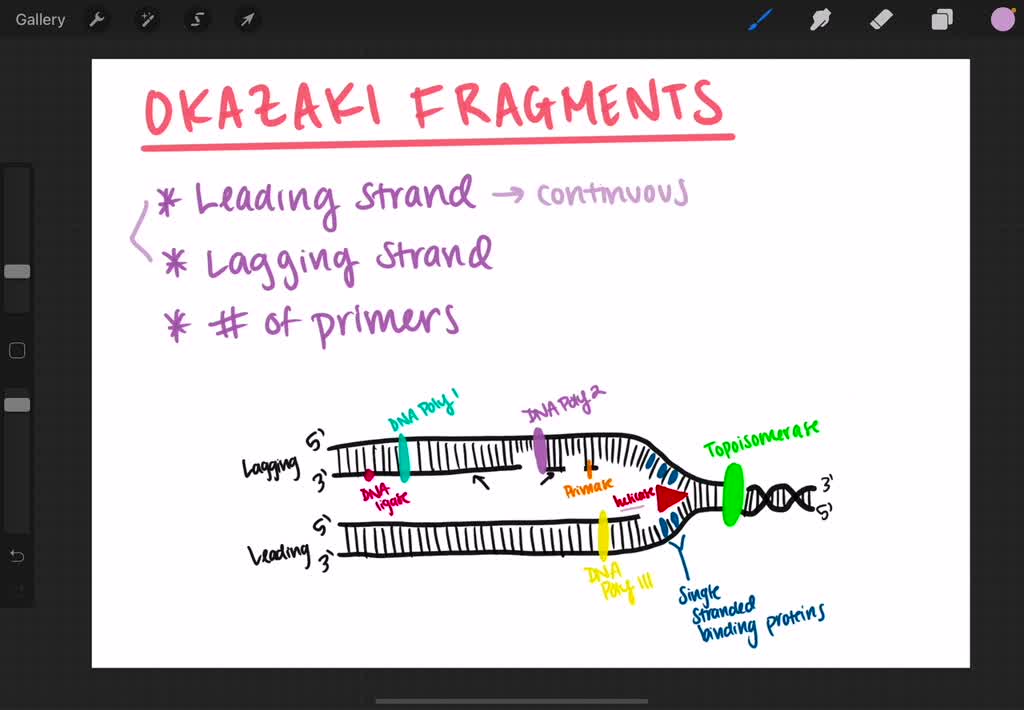
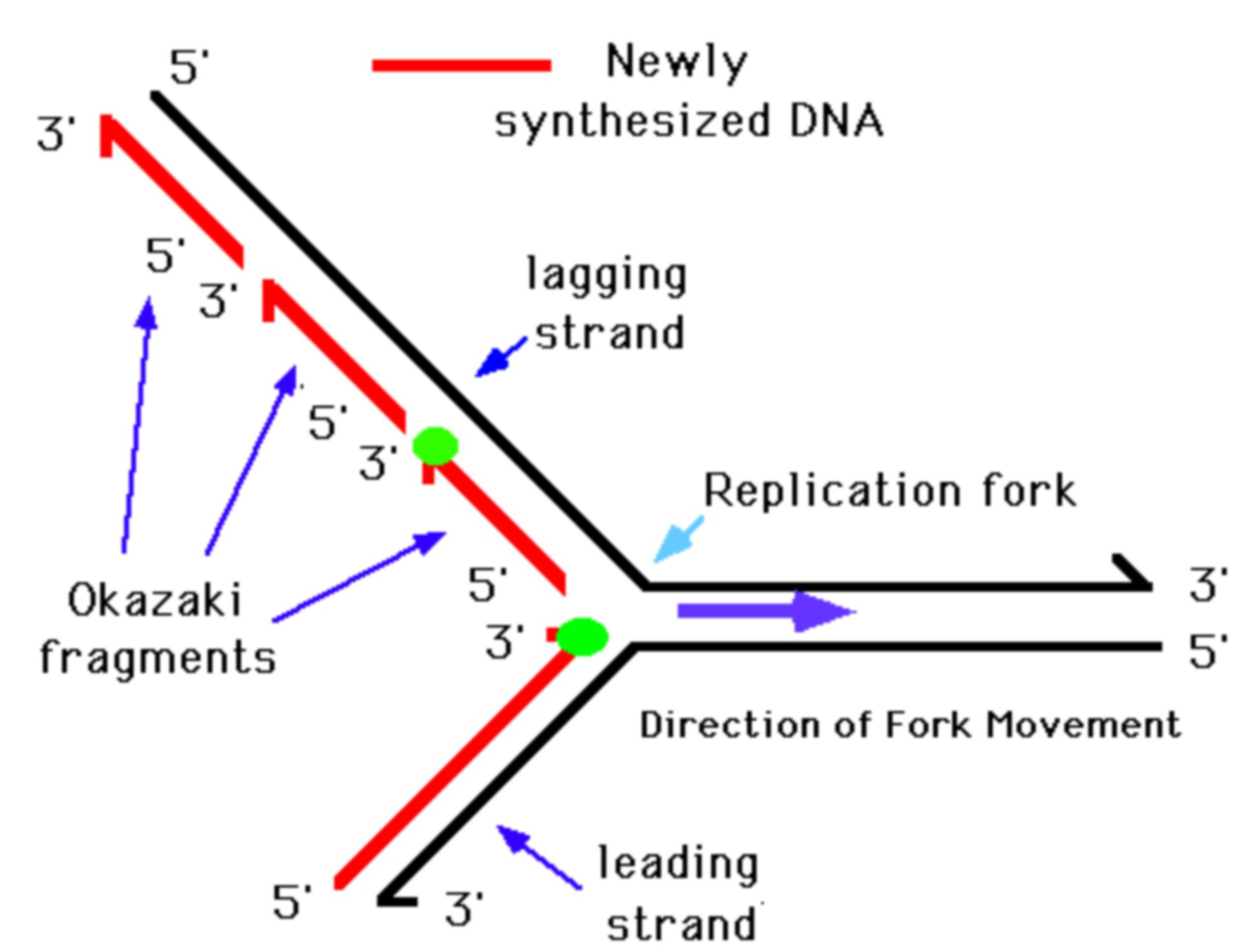
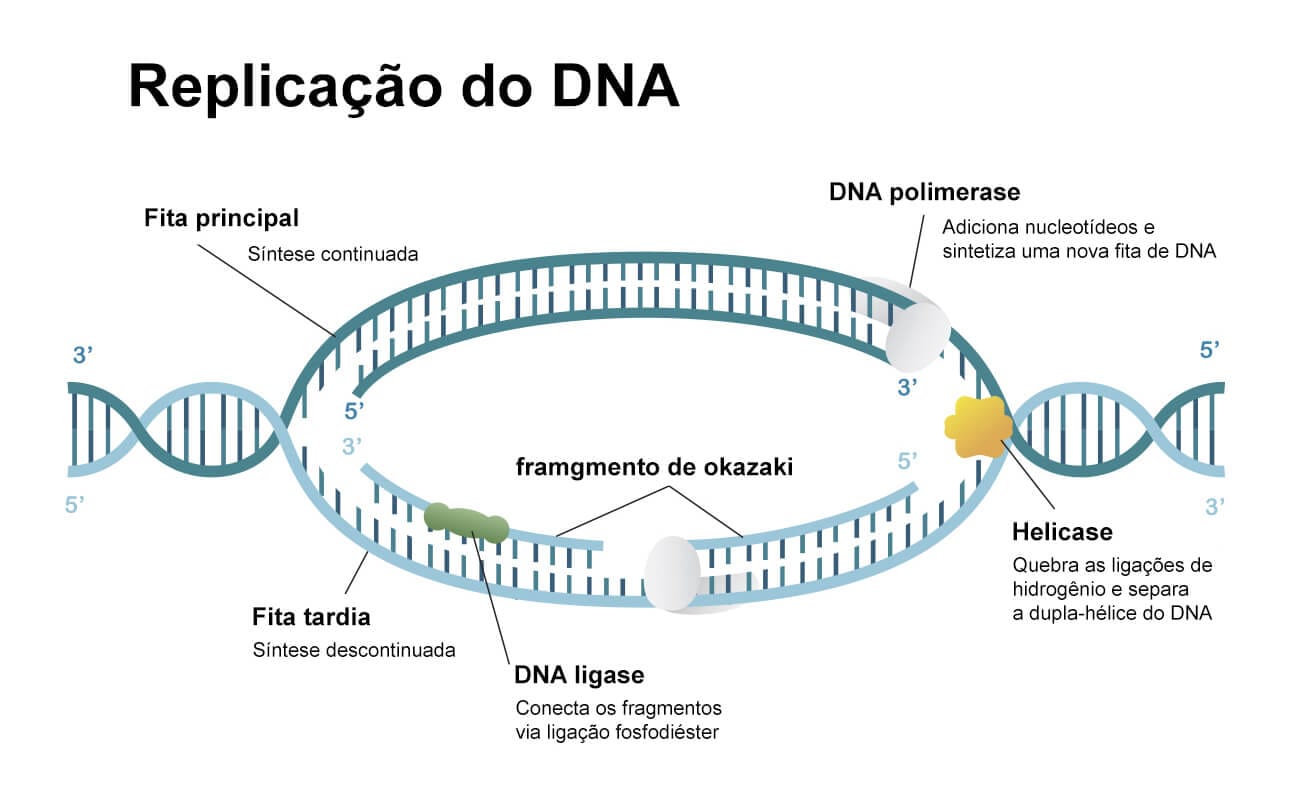
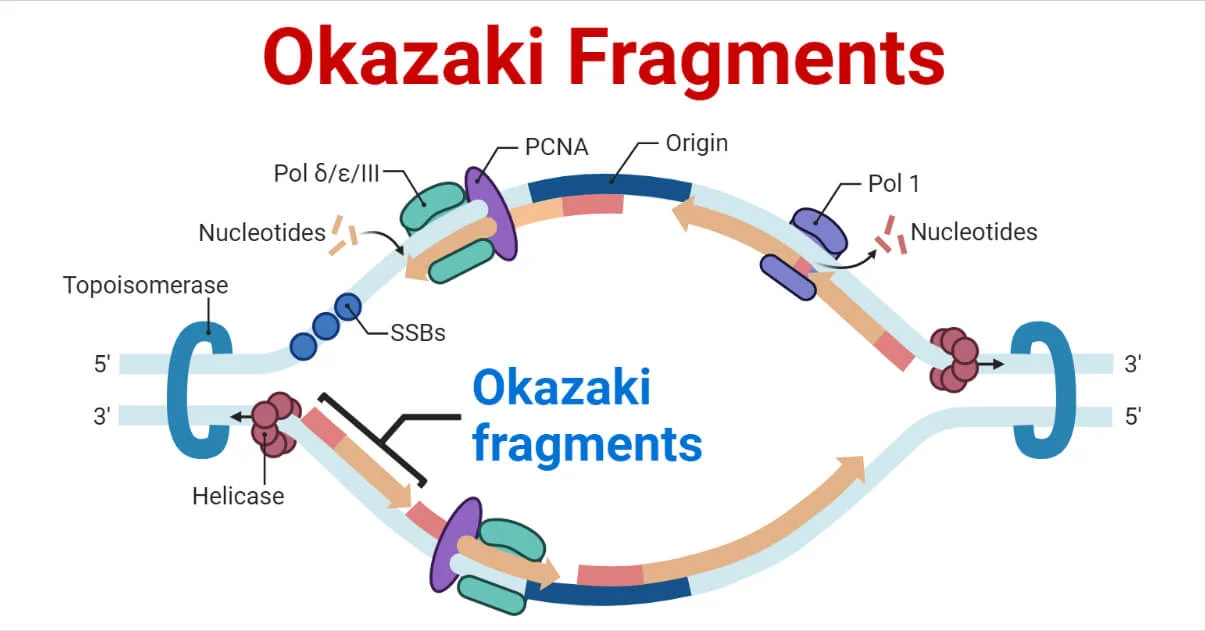
Why Do Okazaki Fragments Form During Dna Replication
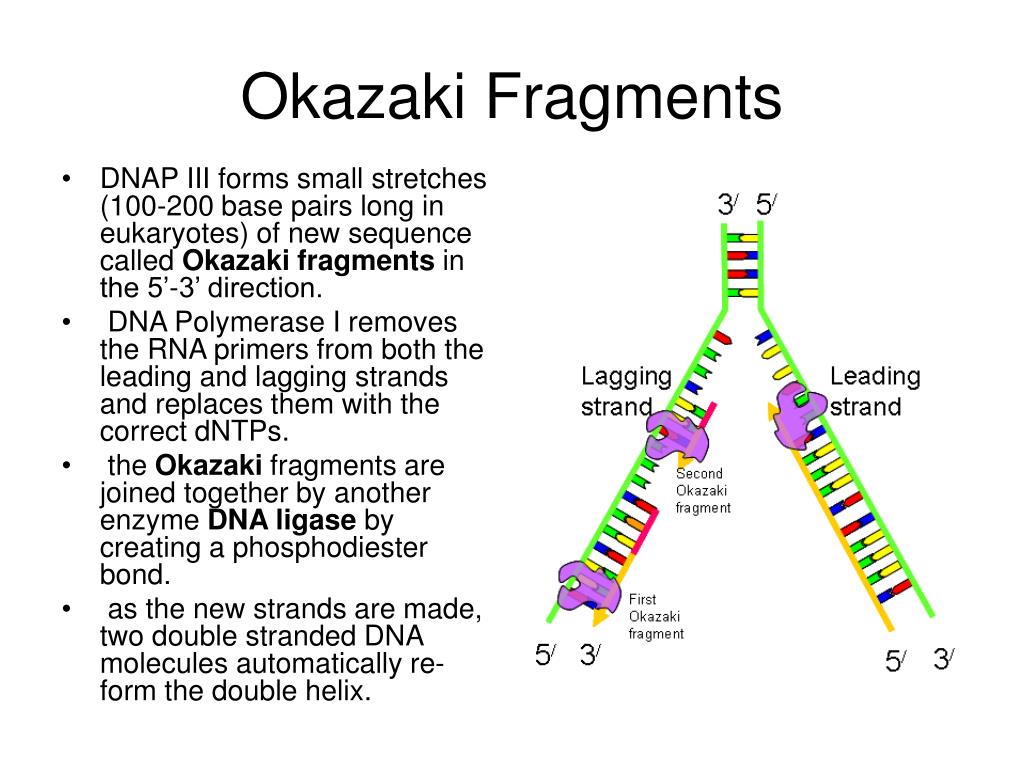
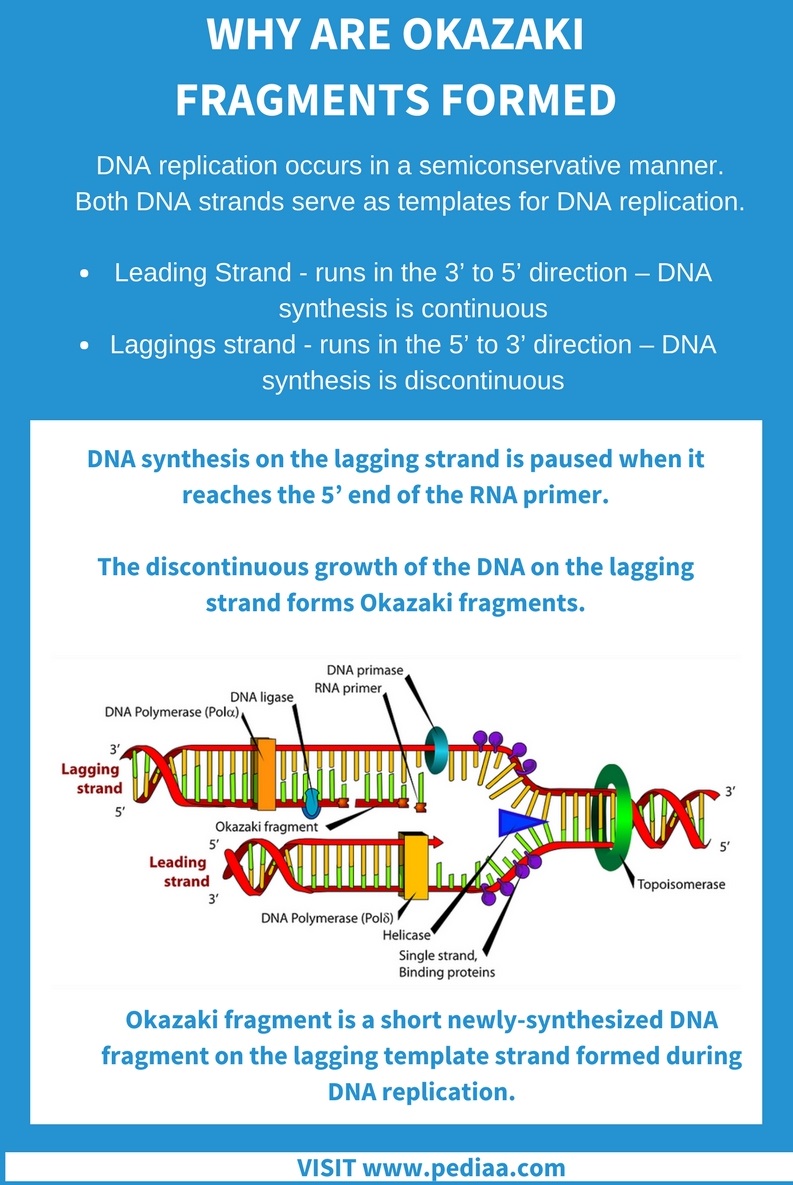
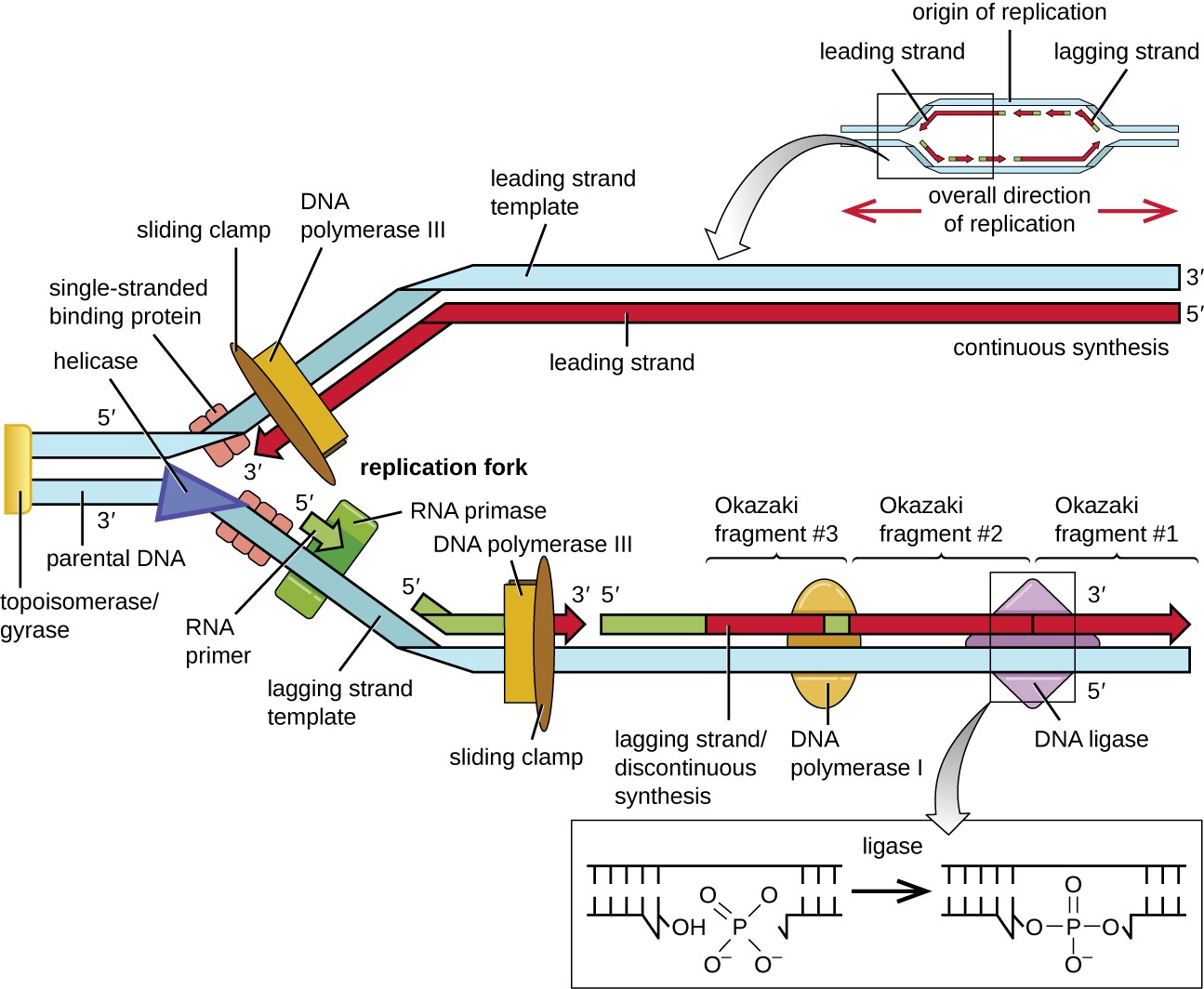
Why Do Okazaki Fragments Form During Dna Replication - Explain the meaning of semiconservative dna replication; The formation of okazaki fragments is a fascinating aspect of dna replication, characterized by a series of orchestrated events. Explain why dna replication is bidirectional and includes both a leading and. Okazaki fragments are short dna sequences synthesized discontinuously on the lagging strand during dna replication, which are.
Okazaki fragments are short dna sequences synthesized discontinuously on the lagging strand during dna replication, which are. Explain the meaning of semiconservative dna replication; Explain why dna replication is bidirectional and includes both a leading and. The formation of okazaki fragments is a fascinating aspect of dna replication, characterized by a series of orchestrated events.
Okazaki fragments are short dna sequences synthesized discontinuously on the lagging strand during dna replication, which are. Explain why dna replication is bidirectional and includes both a leading and. Explain the meaning of semiconservative dna replication; The formation of okazaki fragments is a fascinating aspect of dna replication, characterized by a series of orchestrated events.
Why do okazaki fragments form?
The formation of okazaki fragments is a fascinating aspect of dna replication, characterized by a series of orchestrated events. Explain the meaning of semiconservative dna replication; Okazaki fragments are short dna sequences synthesized discontinuously on the lagging strand during dna replication, which are. Explain why dna replication is bidirectional and includes both a leading and.
What are Okazaki fragments and how they are formed? a. Okazaki
Okazaki fragments are short dna sequences synthesized discontinuously on the lagging strand during dna replication, which are. Explain why dna replication is bidirectional and includes both a leading and. The formation of okazaki fragments is a fascinating aspect of dna replication, characterized by a series of orchestrated events. Explain the meaning of semiconservative dna replication;
Cells Mind Map
Explain the meaning of semiconservative dna replication; Okazaki fragments are short dna sequences synthesized discontinuously on the lagging strand during dna replication, which are. The formation of okazaki fragments is a fascinating aspect of dna replication, characterized by a series of orchestrated events. Explain why dna replication is bidirectional and includes both a leading and.
Genética molecular e o dogma central da biologia molecular
The formation of okazaki fragments is a fascinating aspect of dna replication, characterized by a series of orchestrated events. Explain why dna replication is bidirectional and includes both a leading and. Explain the meaning of semiconservative dna replication; Okazaki fragments are short dna sequences synthesized discontinuously on the lagging strand during dna replication, which are.
قطعات اوکازاکی یک کشف مهم در زیست شناسی مولکولی
Okazaki fragments are short dna sequences synthesized discontinuously on the lagging strand during dna replication, which are. The formation of okazaki fragments is a fascinating aspect of dna replication, characterized by a series of orchestrated events. Explain the meaning of semiconservative dna replication; Explain why dna replication is bidirectional and includes both a leading and.
PPT DNA Replication PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3696728
Explain the meaning of semiconservative dna replication; Explain why dna replication is bidirectional and includes both a leading and. The formation of okazaki fragments is a fascinating aspect of dna replication, characterized by a series of orchestrated events. Okazaki fragments are short dna sequences synthesized discontinuously on the lagging strand during dna replication, which are.
Why are Okazaki Fragments Formed
Explain why dna replication is bidirectional and includes both a leading and. Okazaki fragments are short dna sequences synthesized discontinuously on the lagging strand during dna replication, which are. Explain the meaning of semiconservative dna replication; The formation of okazaki fragments is a fascinating aspect of dna replication, characterized by a series of orchestrated events.
24.1 DNA Replication Biology LibreTexts
The formation of okazaki fragments is a fascinating aspect of dna replication, characterized by a series of orchestrated events. Okazaki fragments are short dna sequences synthesized discontinuously on the lagging strand during dna replication, which are. Explain why dna replication is bidirectional and includes both a leading and. Explain the meaning of semiconservative dna replication;
Okazaki fragment maturation DNA flap dynamics for cell proliferation
Explain why dna replication is bidirectional and includes both a leading and. Okazaki fragments are short dna sequences synthesized discontinuously on the lagging strand during dna replication, which are. Explain the meaning of semiconservative dna replication; The formation of okazaki fragments is a fascinating aspect of dna replication, characterized by a series of orchestrated events.
During DNA replication, Okazaki fragments are used to elongate
Okazaki fragments are short dna sequences synthesized discontinuously on the lagging strand during dna replication, which are. Explain the meaning of semiconservative dna replication; The formation of okazaki fragments is a fascinating aspect of dna replication, characterized by a series of orchestrated events. Explain why dna replication is bidirectional and includes both a leading and.
Okazaki Fragments Are Short Dna Sequences Synthesized Discontinuously On The Lagging Strand During Dna Replication, Which Are.
Explain the meaning of semiconservative dna replication; The formation of okazaki fragments is a fascinating aspect of dna replication, characterized by a series of orchestrated events. Explain why dna replication is bidirectional and includes both a leading and.