Which Situation Occurs When Drugs Cross The Placenta During Pregnancy
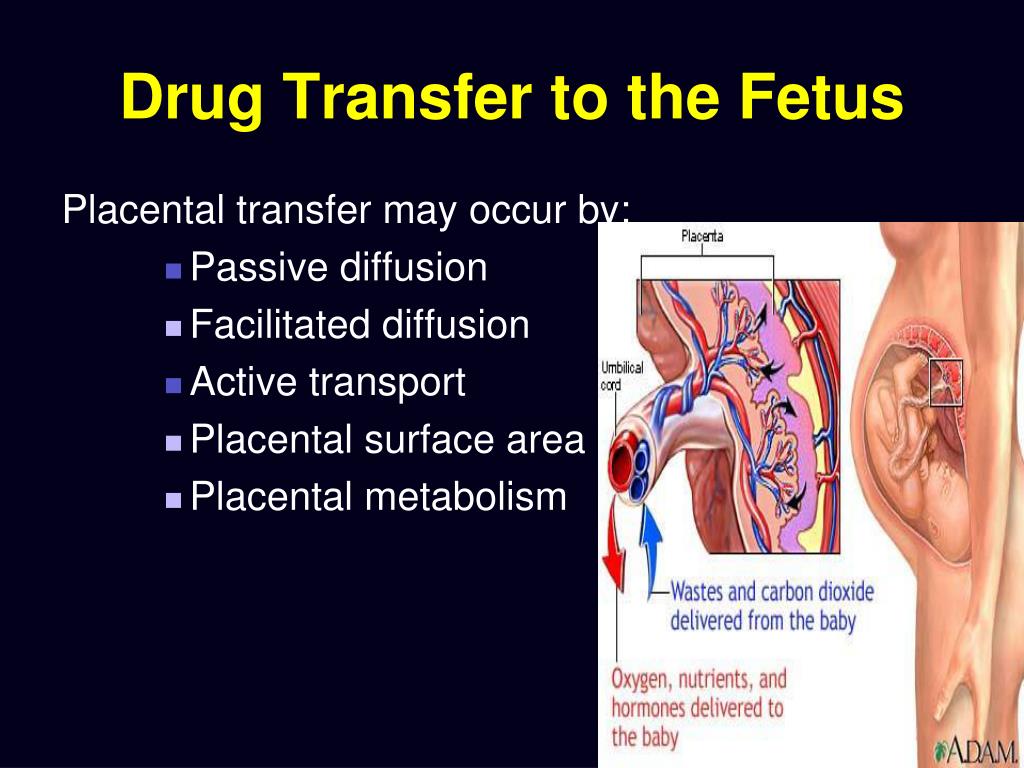
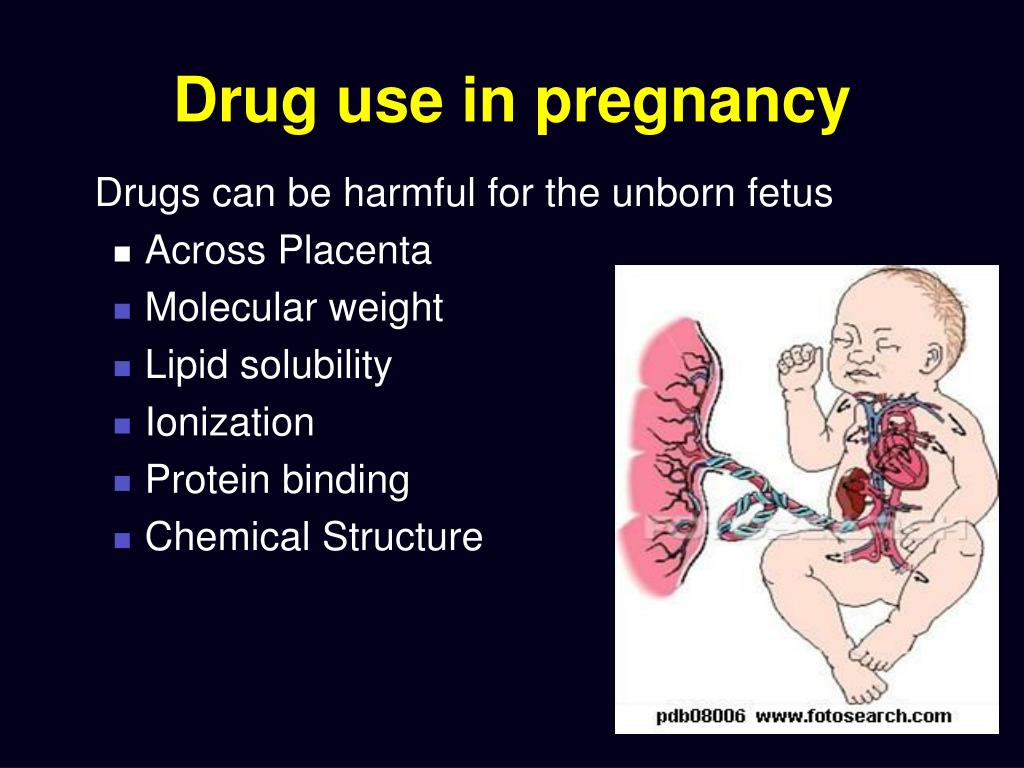
Which Situation Occurs When Drugs Cross The Placenta During Pregnancy - In addition, these drugs were thought to cross the placenta, most probably via diffusion. Ion trapping occurs when maternal alkalosis allows nonionized drugs to cross the placenta, and fetal acidosis. Once inside the developing fetus, the drugs block the uptake. Some drugs that cross the. Not all medications or other substances in the maternal circulation cross the placenta (transfer) to the fetus. Passive diffusion of a drug across the placenta is favored for a drug that is lipophilic, allowing it to cross the phospholipid bilayer. The correct answer is (b).
Passive diffusion of a drug across the placenta is favored for a drug that is lipophilic, allowing it to cross the phospholipid bilayer. Some drugs that cross the. In addition, these drugs were thought to cross the placenta, most probably via diffusion. Ion trapping occurs when maternal alkalosis allows nonionized drugs to cross the placenta, and fetal acidosis. Once inside the developing fetus, the drugs block the uptake. The correct answer is (b). Not all medications or other substances in the maternal circulation cross the placenta (transfer) to the fetus.
Once inside the developing fetus, the drugs block the uptake. Ion trapping occurs when maternal alkalosis allows nonionized drugs to cross the placenta, and fetal acidosis. Not all medications or other substances in the maternal circulation cross the placenta (transfer) to the fetus. Passive diffusion of a drug across the placenta is favored for a drug that is lipophilic, allowing it to cross the phospholipid bilayer. Some drugs that cross the. The correct answer is (b). In addition, these drugs were thought to cross the placenta, most probably via diffusion.
PPT Teratogens and drugs of abuse in pregnancy PowerPoint
Once inside the developing fetus, the drugs block the uptake. Some drugs that cross the. Ion trapping occurs when maternal alkalosis allows nonionized drugs to cross the placenta, and fetal acidosis. The correct answer is (b). Not all medications or other substances in the maternal circulation cross the placenta (transfer) to the fetus.
Pregnancy With Drugs
Once inside the developing fetus, the drugs block the uptake. The correct answer is (b). Some drugs that cross the. Passive diffusion of a drug across the placenta is favored for a drug that is lipophilic, allowing it to cross the phospholipid bilayer. In addition, these drugs were thought to cross the placenta, most probably via diffusion.
Pregnancy and pharmacology
Once inside the developing fetus, the drugs block the uptake. Passive diffusion of a drug across the placenta is favored for a drug that is lipophilic, allowing it to cross the phospholipid bilayer. The correct answer is (b). Not all medications or other substances in the maternal circulation cross the placenta (transfer) to the fetus. In addition, these drugs were.
Medications during pregnancy
The correct answer is (b). Once inside the developing fetus, the drugs block the uptake. Passive diffusion of a drug across the placenta is favored for a drug that is lipophilic, allowing it to cross the phospholipid bilayer. In addition, these drugs were thought to cross the placenta, most probably via diffusion. Ion trapping occurs when maternal alkalosis allows nonionized.
PPT EFFECT OF MATERNAL DRUGS ON FETUS PowerPoint Presentation, free
Passive diffusion of a drug across the placenta is favored for a drug that is lipophilic, allowing it to cross the phospholipid bilayer. Some drugs that cross the. In addition, these drugs were thought to cross the placenta, most probably via diffusion. The correct answer is (b). Not all medications or other substances in the maternal circulation cross the placenta.
PPT EFFECT OF MATERNAL DRUGS ON FETUS PowerPoint Presentation, free
The correct answer is (b). In addition, these drugs were thought to cross the placenta, most probably via diffusion. Passive diffusion of a drug across the placenta is favored for a drug that is lipophilic, allowing it to cross the phospholipid bilayer. Some drugs that cross the. Once inside the developing fetus, the drugs block the uptake.
Drugs safety in pregnancy
Not all medications or other substances in the maternal circulation cross the placenta (transfer) to the fetus. In addition, these drugs were thought to cross the placenta, most probably via diffusion. The correct answer is (b). Some drugs that cross the. Ion trapping occurs when maternal alkalosis allows nonionized drugs to cross the placenta, and fetal acidosis.
Drug transport across the human placenta review of placentaonachip
The correct answer is (b). Ion trapping occurs when maternal alkalosis allows nonionized drugs to cross the placenta, and fetal acidosis. Some drugs that cross the. Once inside the developing fetus, the drugs block the uptake. Not all medications or other substances in the maternal circulation cross the placenta (transfer) to the fetus.
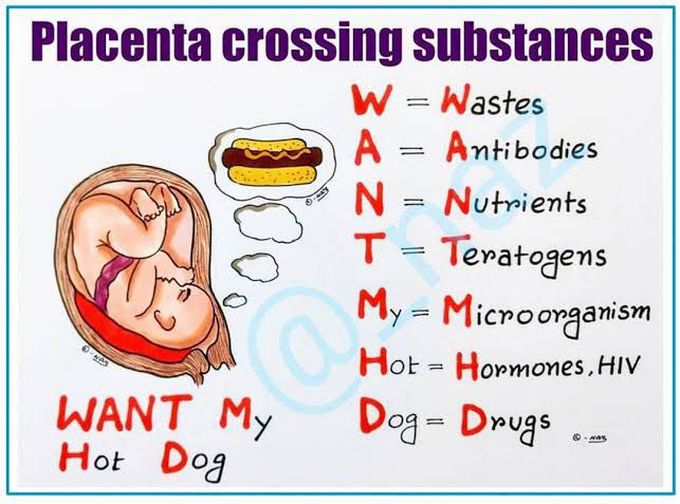
Placenta crossing substances MEDizzy
Ion trapping occurs when maternal alkalosis allows nonionized drugs to cross the placenta, and fetal acidosis. Passive diffusion of a drug across the placenta is favored for a drug that is lipophilic, allowing it to cross the phospholipid bilayer. Some drugs that cross the. Not all medications or other substances in the maternal circulation cross the placenta (transfer) to the.
Drugs safety in pregnancy
The correct answer is (b). Once inside the developing fetus, the drugs block the uptake. Some drugs that cross the. In addition, these drugs were thought to cross the placenta, most probably via diffusion. Passive diffusion of a drug across the placenta is favored for a drug that is lipophilic, allowing it to cross the phospholipid bilayer.
The Correct Answer Is (B).
Ion trapping occurs when maternal alkalosis allows nonionized drugs to cross the placenta, and fetal acidosis. Some drugs that cross the. Once inside the developing fetus, the drugs block the uptake. Not all medications or other substances in the maternal circulation cross the placenta (transfer) to the fetus.
Passive Diffusion Of A Drug Across The Placenta Is Favored For A Drug That Is Lipophilic, Allowing It To Cross The Phospholipid Bilayer.
In addition, these drugs were thought to cross the placenta, most probably via diffusion.