What Are The Four Nitrogenous Bases Found In Rna
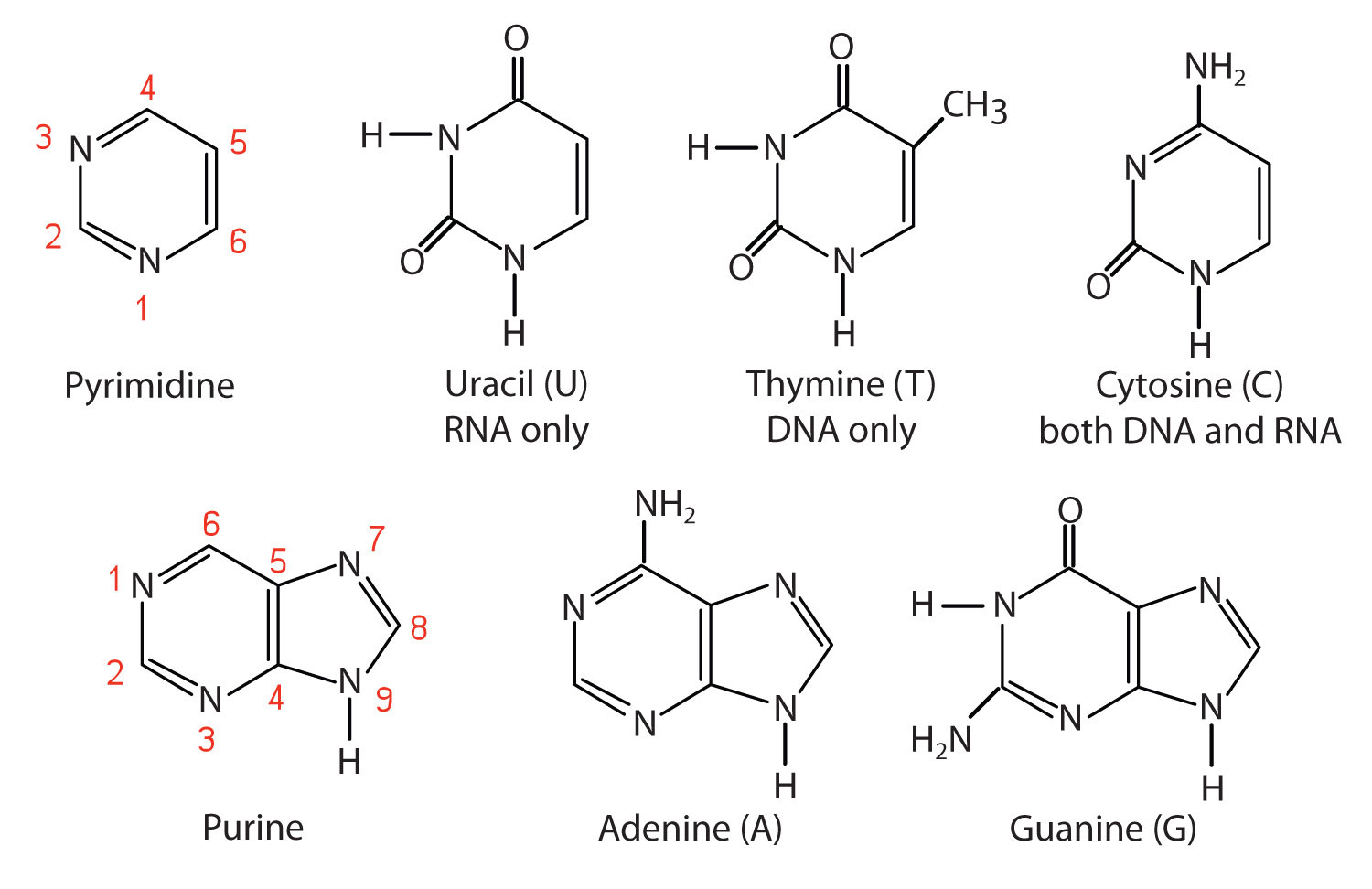
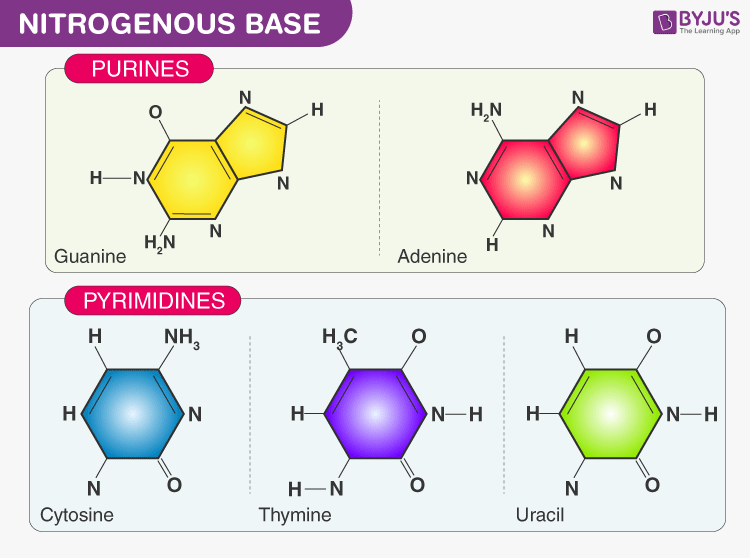
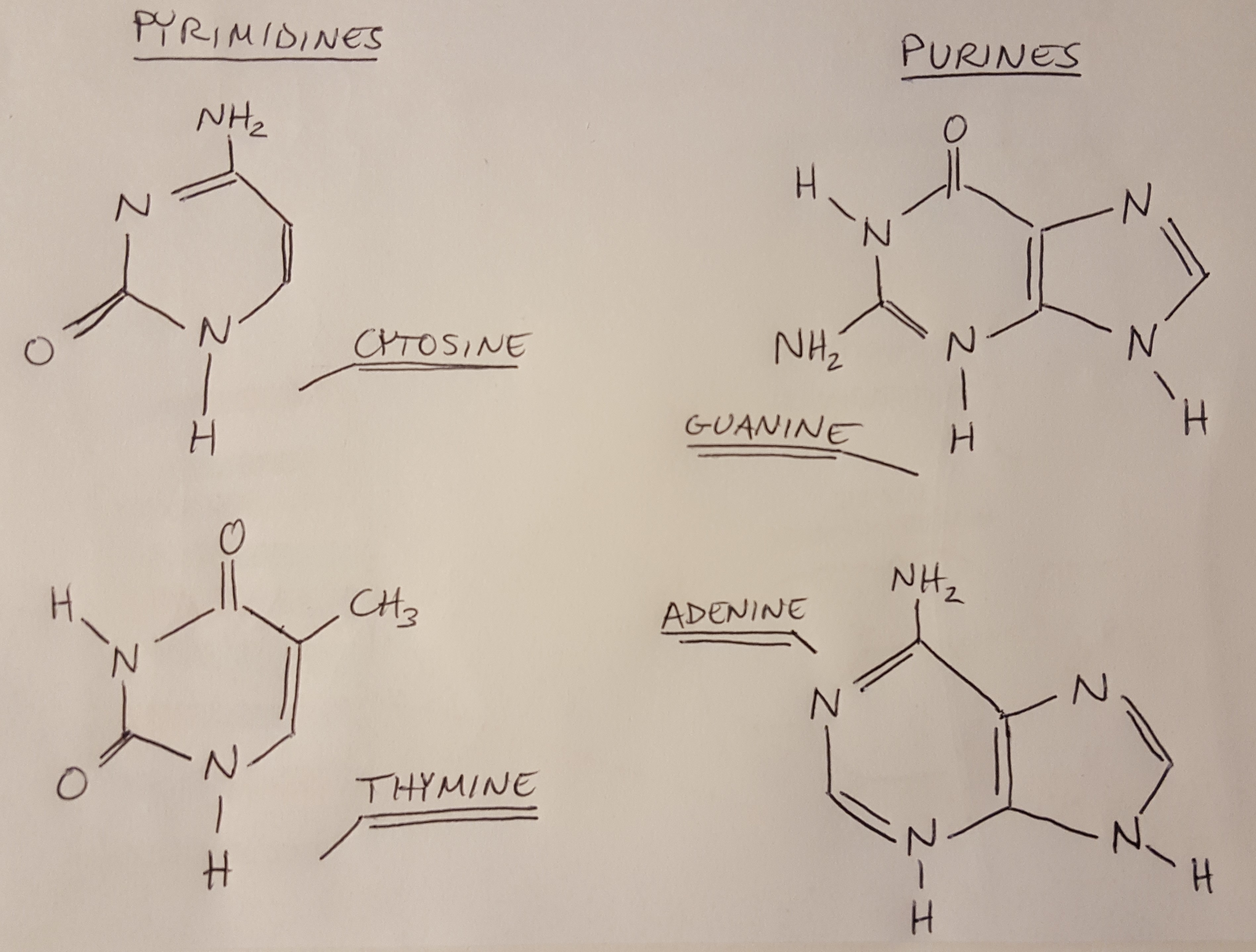
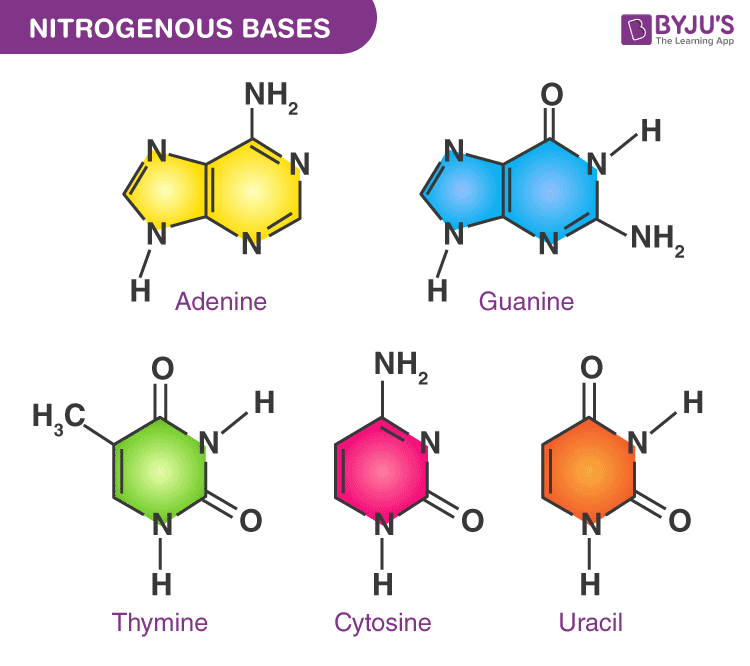
What Are The Four Nitrogenous Bases Found In Rna - Rna consists of four nitrogenous bases: What are the four nitrogenous bases found in rna? Uracil is a pyrimidine that is structurally similar to the. Dna attains a secondary structure when hydrogen bonds form. Adenine, cytosine, uracil, and guanine.
Dna attains a secondary structure when hydrogen bonds form. What are the four nitrogenous bases found in rna? Rna consists of four nitrogenous bases: Uracil is a pyrimidine that is structurally similar to the. Adenine, cytosine, uracil, and guanine.
Dna attains a secondary structure when hydrogen bonds form. Rna consists of four nitrogenous bases: Adenine, cytosine, uracil, and guanine. What are the four nitrogenous bases found in rna? Uracil is a pyrimidine that is structurally similar to the.
The Nitrogenous Bases Used In Protein Synthesis We Are Eaton
Adenine, cytosine, uracil, and guanine. Dna attains a secondary structure when hydrogen bonds form. What are the four nitrogenous bases found in rna? Rna consists of four nitrogenous bases: Uracil is a pyrimidine that is structurally similar to the.
shortcut to identify Nitrogenous bases(cytosine and co) r/Mcat
Adenine, cytosine, uracil, and guanine. Dna attains a secondary structure when hydrogen bonds form. Rna consists of four nitrogenous bases: What are the four nitrogenous bases found in rna? Uracil is a pyrimidine that is structurally similar to the.
19.1 Nucleotides The Basics of General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
Rna consists of four nitrogenous bases: What are the four nitrogenous bases found in rna? Adenine, cytosine, uracil, and guanine. Dna attains a secondary structure when hydrogen bonds form. Uracil is a pyrimidine that is structurally similar to the.
Which Pair Of Nitrogenous Bases Will Form A Bond In A Dna Molecule
What are the four nitrogenous bases found in rna? Rna consists of four nitrogenous bases: Uracil is a pyrimidine that is structurally similar to the. Adenine, cytosine, uracil, and guanine. Dna attains a secondary structure when hydrogen bonds form.
Solved 14. What are the four nitrogenous bases found in RNA?
Rna consists of four nitrogenous bases: What are the four nitrogenous bases found in rna? Uracil is a pyrimidine that is structurally similar to the. Adenine, cytosine, uracil, and guanine. Dna attains a secondary structure when hydrogen bonds form.
What Nitrogenous Bases Are Found in DNA? Get the Answer at BYJU'S NEET
Uracil is a pyrimidine that is structurally similar to the. Dna attains a secondary structure when hydrogen bonds form. Adenine, cytosine, uracil, and guanine. What are the four nitrogenous bases found in rna? Rna consists of four nitrogenous bases:
Nitrogen Base Structure
What are the four nitrogenous bases found in rna? Uracil is a pyrimidine that is structurally similar to the. Adenine, cytosine, uracil, and guanine. Dna attains a secondary structure when hydrogen bonds form. Rna consists of four nitrogenous bases:
Types of Nitrogenous Bases In RNA Detailed Facts Lambda Geeks
Rna consists of four nitrogenous bases: Dna attains a secondary structure when hydrogen bonds form. Adenine, cytosine, uracil, and guanine. What are the four nitrogenous bases found in rna? Uracil is a pyrimidine that is structurally similar to the.
Nitrogen Base Definition In Biology at Mary Murphy blog
Dna attains a secondary structure when hydrogen bonds form. Adenine, cytosine, uracil, and guanine. What are the four nitrogenous bases found in rna? Uracil is a pyrimidine that is structurally similar to the. Rna consists of four nitrogenous bases:
RNA. Structure, Transcription and Editing Presentation Biology
Uracil is a pyrimidine that is structurally similar to the. Adenine, cytosine, uracil, and guanine. Dna attains a secondary structure when hydrogen bonds form. What are the four nitrogenous bases found in rna? Rna consists of four nitrogenous bases:
Uracil Is A Pyrimidine That Is Structurally Similar To The.
What are the four nitrogenous bases found in rna? Rna consists of four nitrogenous bases: Dna attains a secondary structure when hydrogen bonds form. Adenine, cytosine, uracil, and guanine.




.PNG)