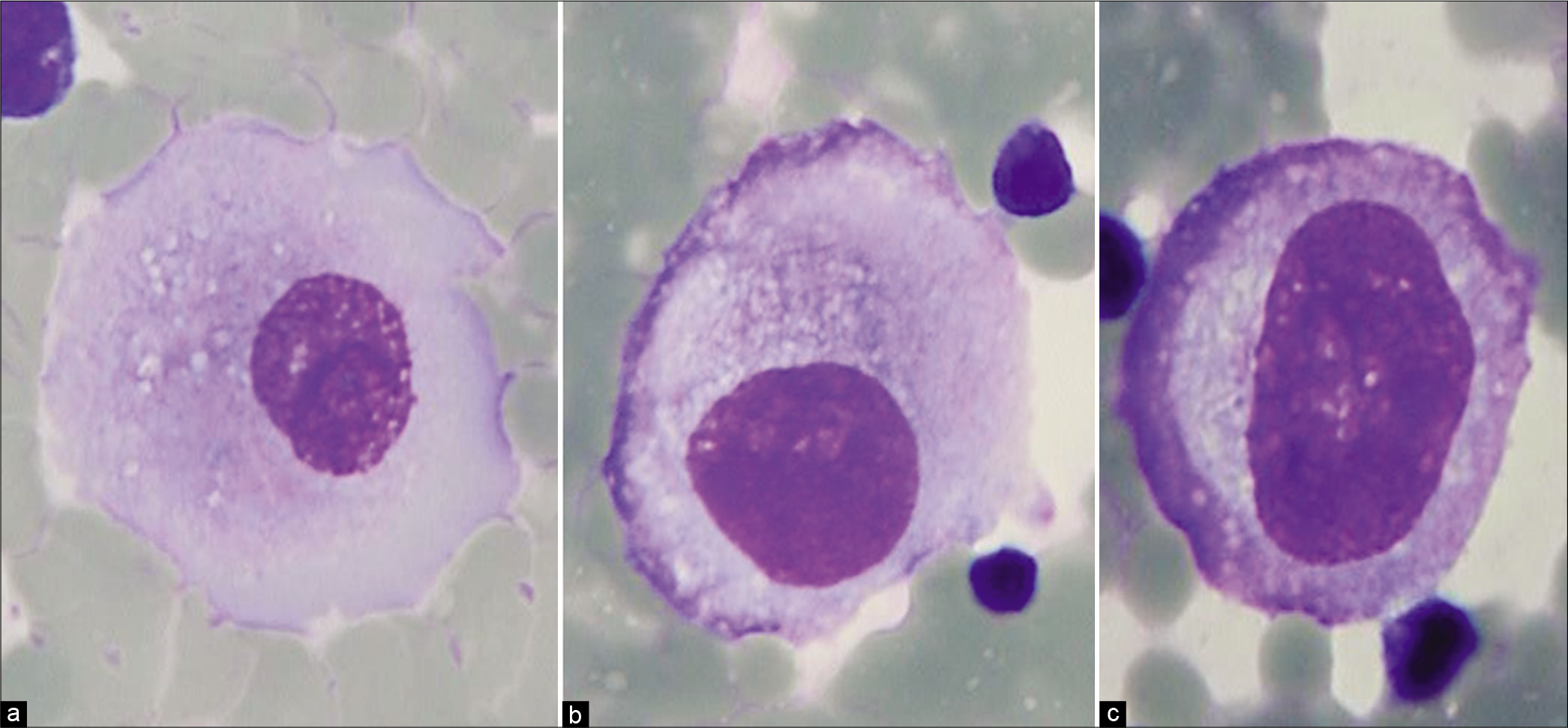
What Are Reactive Mesothelial Cells
What Are Reactive Mesothelial Cells - Infection, inflammation, infarction, liver disease, radiation,. They form a barrier on the outside of. Mesothelial cells are the cells that cover our internal organs such as our lungs, liver, stomach, and colon. When, because of inexperience or diffidence, the cytologic picture remains unsolved or ambiguous or when mesothelial cells appear to be. All effusions in serous cavities represent a pathologic processes secondary to inflammatory, neoplastic, hemodynamic, or. There are many causes of reactive mesothelial cells including: Some floridly reactive mesothelial cells with hyperchromatic enlarged nuclei with prominent nucleoli and scant cytoplasm may resemble.
They form a barrier on the outside of. When, because of inexperience or diffidence, the cytologic picture remains unsolved or ambiguous or when mesothelial cells appear to be. Infection, inflammation, infarction, liver disease, radiation,. All effusions in serous cavities represent a pathologic processes secondary to inflammatory, neoplastic, hemodynamic, or. Mesothelial cells are the cells that cover our internal organs such as our lungs, liver, stomach, and colon. There are many causes of reactive mesothelial cells including: Some floridly reactive mesothelial cells with hyperchromatic enlarged nuclei with prominent nucleoli and scant cytoplasm may resemble.
When, because of inexperience or diffidence, the cytologic picture remains unsolved or ambiguous or when mesothelial cells appear to be. Some floridly reactive mesothelial cells with hyperchromatic enlarged nuclei with prominent nucleoli and scant cytoplasm may resemble. Infection, inflammation, infarction, liver disease, radiation,. Mesothelial cells are the cells that cover our internal organs such as our lungs, liver, stomach, and colon. All effusions in serous cavities represent a pathologic processes secondary to inflammatory, neoplastic, hemodynamic, or. They form a barrier on the outside of. There are many causes of reactive mesothelial cells including:
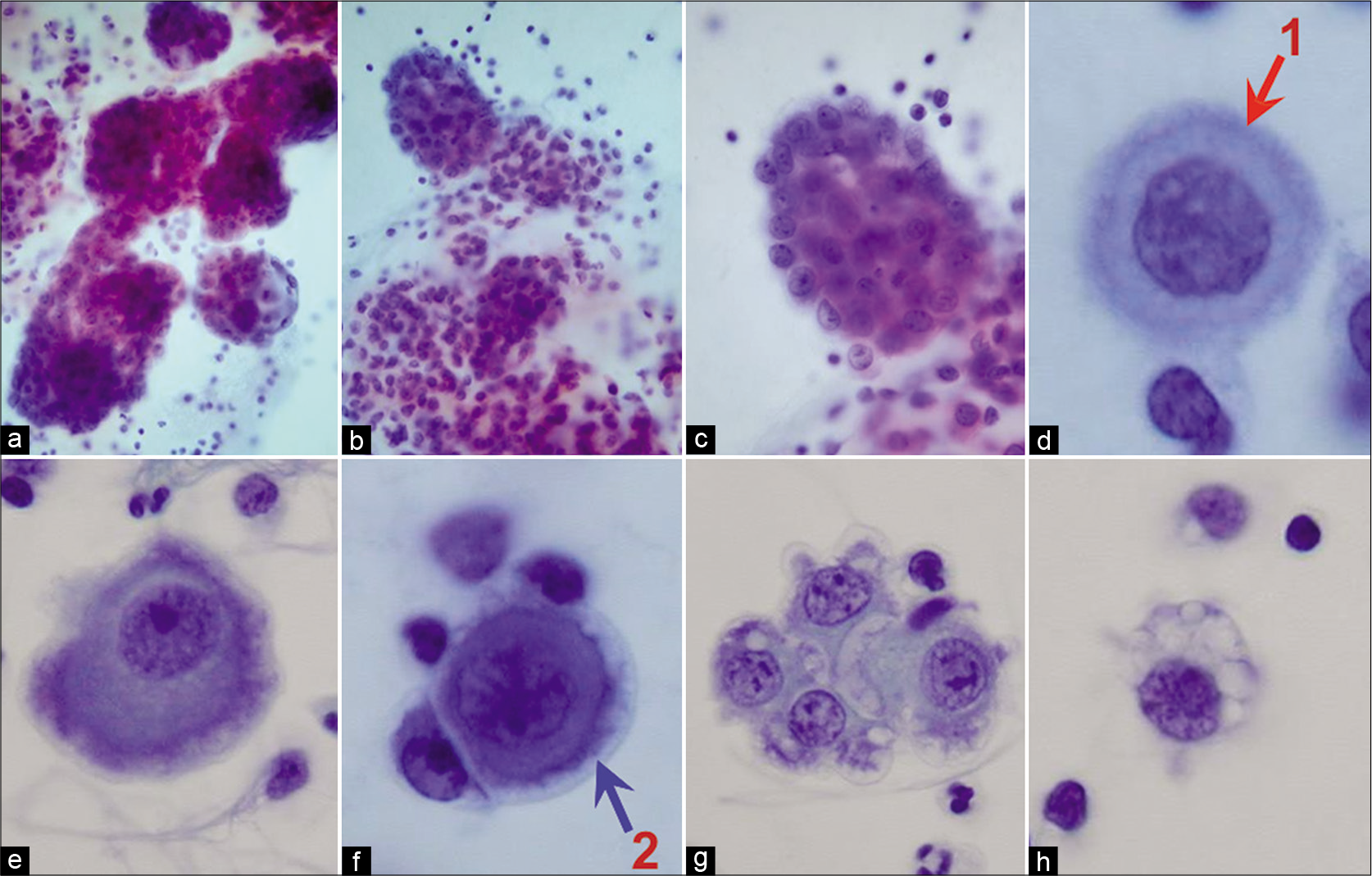
The panorama of different faces of mesothelial cells CytoJournal
All effusions in serous cavities represent a pathologic processes secondary to inflammatory, neoplastic, hemodynamic, or. Some floridly reactive mesothelial cells with hyperchromatic enlarged nuclei with prominent nucleoli and scant cytoplasm may resemble. They form a barrier on the outside of. There are many causes of reactive mesothelial cells including: When, because of inexperience or diffidence, the cytologic picture remains unsolved.
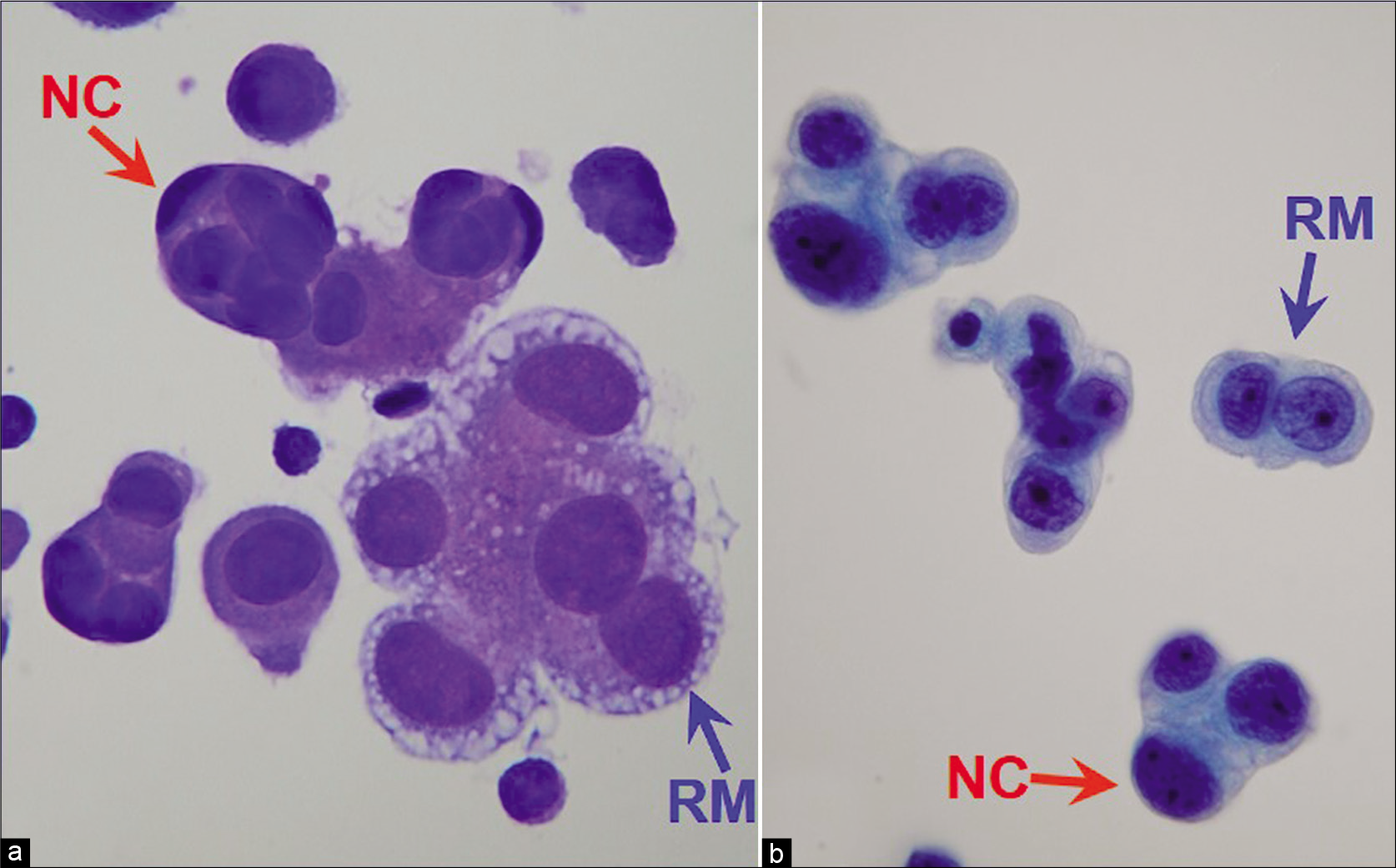
The Carcinoma vs. Reactive Mesothelial Cell Conundrum
All effusions in serous cavities represent a pathologic processes secondary to inflammatory, neoplastic, hemodynamic, or. When, because of inexperience or diffidence, the cytologic picture remains unsolved or ambiguous or when mesothelial cells appear to be. Infection, inflammation, infarction, liver disease, radiation,. Mesothelial cells are the cells that cover our internal organs such as our lungs, liver, stomach, and colon. There.
Reactive mesothelial cells with atypia. Mesothelial cells may contain
When, because of inexperience or diffidence, the cytologic picture remains unsolved or ambiguous or when mesothelial cells appear to be. Mesothelial cells are the cells that cover our internal organs such as our lungs, liver, stomach, and colon. They form a barrier on the outside of. There are many causes of reactive mesothelial cells including: Some floridly reactive mesothelial cells.
Reactive mesothelial cell paracentesis (ascities) 100x giemsa stain
All effusions in serous cavities represent a pathologic processes secondary to inflammatory, neoplastic, hemodynamic, or. Infection, inflammation, infarction, liver disease, radiation,. When, because of inexperience or diffidence, the cytologic picture remains unsolved or ambiguous or when mesothelial cells appear to be. There are many causes of reactive mesothelial cells including: They form a barrier on the outside of.
Reactive Mesothelial Cell (x100, oil) r/microscopy
Some floridly reactive mesothelial cells with hyperchromatic enlarged nuclei with prominent nucleoli and scant cytoplasm may resemble. They form a barrier on the outside of. There are many causes of reactive mesothelial cells including: All effusions in serous cavities represent a pathologic processes secondary to inflammatory, neoplastic, hemodynamic, or. Mesothelial cells are the cells that cover our internal organs such.
Mesothelial Cells
All effusions in serous cavities represent a pathologic processes secondary to inflammatory, neoplastic, hemodynamic, or. When, because of inexperience or diffidence, the cytologic picture remains unsolved or ambiguous or when mesothelial cells appear to be. Some floridly reactive mesothelial cells with hyperchromatic enlarged nuclei with prominent nucleoli and scant cytoplasm may resemble. They form a barrier on the outside of..
Mesothelioma Vs Reactive Mesothelial Cells Cytology 2022E Jurnal
They form a barrier on the outside of. All effusions in serous cavities represent a pathologic processes secondary to inflammatory, neoplastic, hemodynamic, or. Infection, inflammation, infarction, liver disease, radiation,. Some floridly reactive mesothelial cells with hyperchromatic enlarged nuclei with prominent nucleoli and scant cytoplasm may resemble. There are many causes of reactive mesothelial cells including:
Mesothelioma Vs Reactive Mesothelial Cells Cytology 2022E Jurnal
They form a barrier on the outside of. All effusions in serous cavities represent a pathologic processes secondary to inflammatory, neoplastic, hemodynamic, or. Some floridly reactive mesothelial cells with hyperchromatic enlarged nuclei with prominent nucleoli and scant cytoplasm may resemble. There are many causes of reactive mesothelial cells including: Mesothelial cells are the cells that cover our internal organs such.
Mesothelial Cells
Some floridly reactive mesothelial cells with hyperchromatic enlarged nuclei with prominent nucleoli and scant cytoplasm may resemble. Mesothelial cells are the cells that cover our internal organs such as our lungs, liver, stomach, and colon. There are many causes of reactive mesothelial cells including: Infection, inflammation, infarction, liver disease, radiation,. When, because of inexperience or diffidence, the cytologic picture remains.
[PDF] A Cytological Study to Differentiate Between Reactive Mesothelial
When, because of inexperience or diffidence, the cytologic picture remains unsolved or ambiguous or when mesothelial cells appear to be. There are many causes of reactive mesothelial cells including: All effusions in serous cavities represent a pathologic processes secondary to inflammatory, neoplastic, hemodynamic, or. Some floridly reactive mesothelial cells with hyperchromatic enlarged nuclei with prominent nucleoli and scant cytoplasm may.
Some Floridly Reactive Mesothelial Cells With Hyperchromatic Enlarged Nuclei With Prominent Nucleoli And Scant Cytoplasm May Resemble.
All effusions in serous cavities represent a pathologic processes secondary to inflammatory, neoplastic, hemodynamic, or. There are many causes of reactive mesothelial cells including: They form a barrier on the outside of. Infection, inflammation, infarction, liver disease, radiation,.
When, Because Of Inexperience Or Diffidence, The Cytologic Picture Remains Unsolved Or Ambiguous Or When Mesothelial Cells Appear To Be.
Mesothelial cells are the cells that cover our internal organs such as our lungs, liver, stomach, and colon.





![[PDF] A Cytological Study to Differentiate Between Reactive Mesothelial](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/309669c742c037479ee338843c7b569db981a7d3/4-Figure4-1.png)