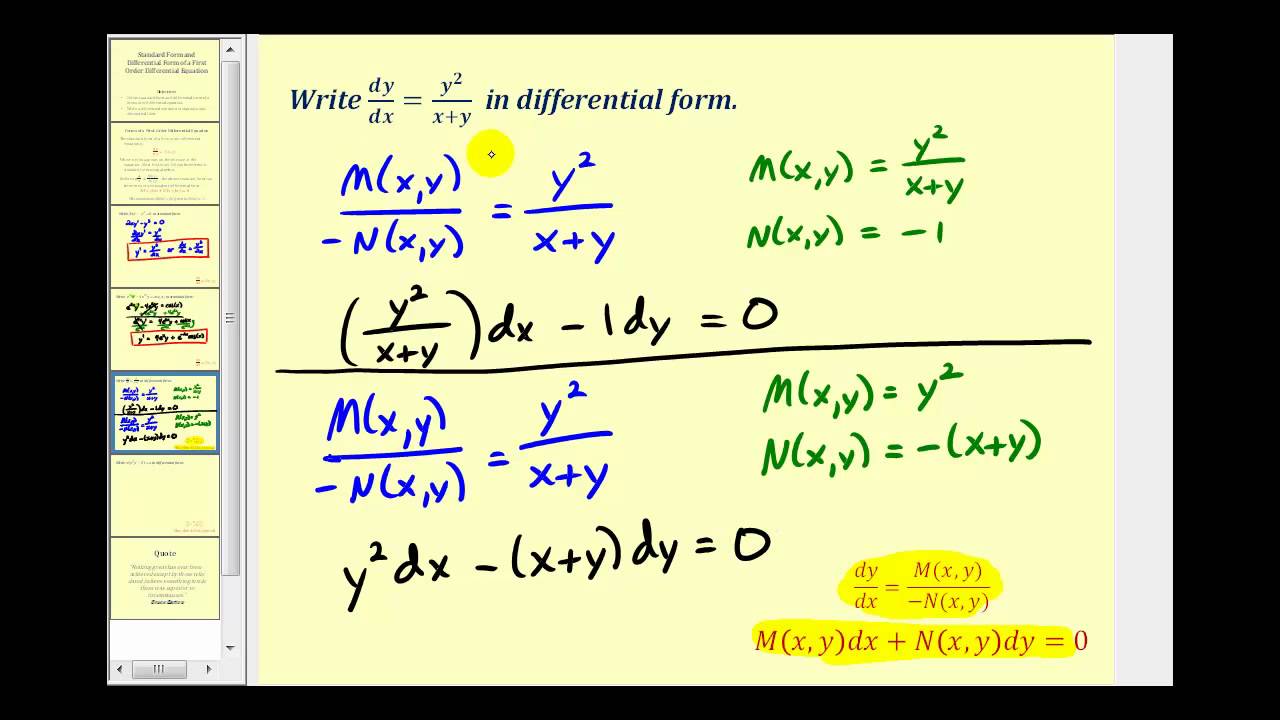
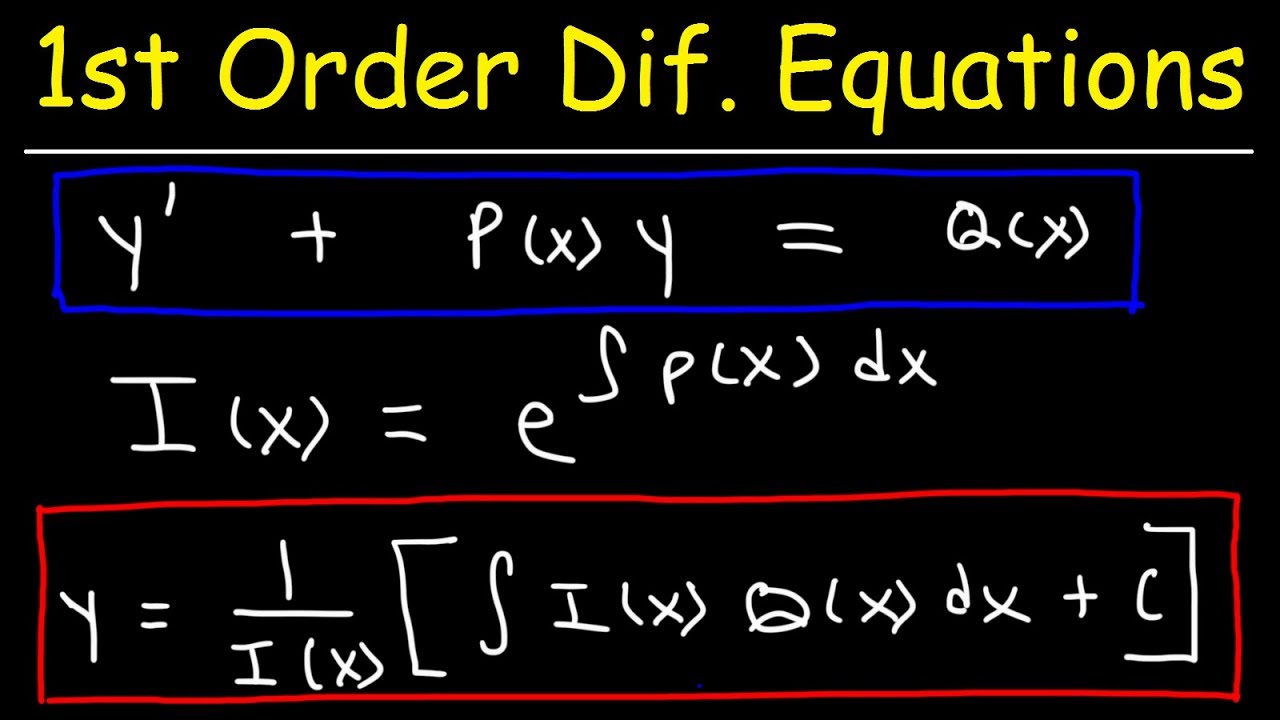
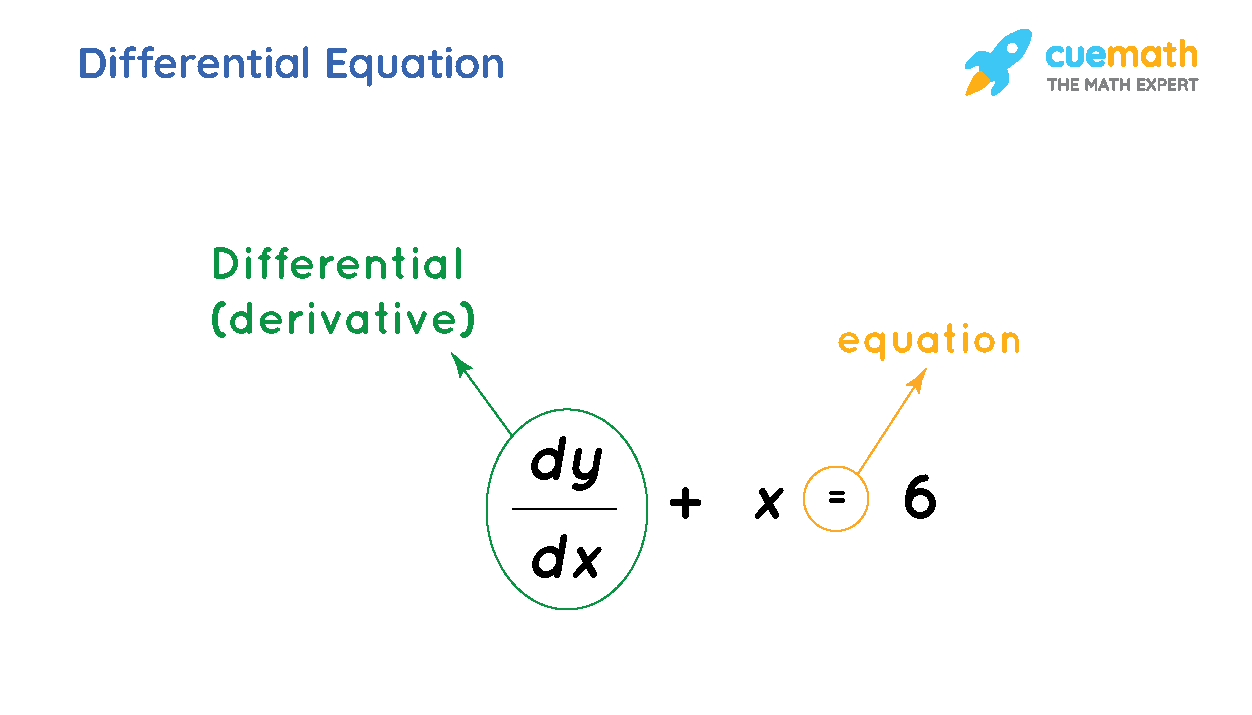
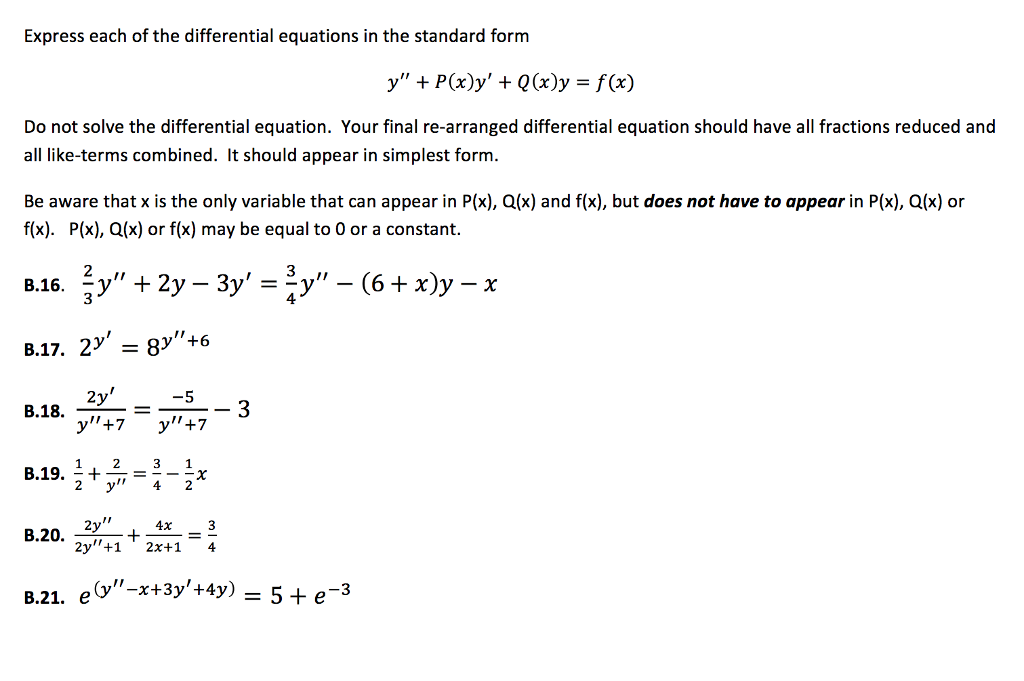
Standard Form Of Differential Equation
Standard Form Of Differential Equation - A differential equation can be identified as a first order linear differential equation using its standard form: It is useful to have the coefficient of y be equal to 1. The standard form of a linear differential equation is dy/dx + py = q, and it contains the variable y, and its derivatives. The p and q in this. Our main goal in this section is to derive a solution method for equations of this form.
Our main goal in this section is to derive a solution method for equations of this form. The standard form of a linear differential equation is dy/dx + py = q, and it contains the variable y, and its derivatives. It is useful to have the coefficient of y be equal to 1. A differential equation can be identified as a first order linear differential equation using its standard form: The p and q in this.
It is useful to have the coefficient of y be equal to 1. The standard form of a linear differential equation is dy/dx + py = q, and it contains the variable y, and its derivatives. A differential equation can be identified as a first order linear differential equation using its standard form: The p and q in this. Our main goal in this section is to derive a solution method for equations of this form.
Standard and Differential Form of FirstOrder Differential Equations
Our main goal in this section is to derive a solution method for equations of this form. A differential equation can be identified as a first order linear differential equation using its standard form: The standard form of a linear differential equation is dy/dx + py = q, and it contains the variable y, and its derivatives. It is useful.
First Order Linear Differential Equations YouTube
The p and q in this. Our main goal in this section is to derive a solution method for equations of this form. It is useful to have the coefficient of y be equal to 1. The standard form of a linear differential equation is dy/dx + py = q, and it contains the variable y, and its derivatives. A.
Solving a First Order Linear Differential Equation YouTube
The standard form of a linear differential equation is dy/dx + py = q, and it contains the variable y, and its derivatives. A differential equation can be identified as a first order linear differential equation using its standard form: The p and q in this. Our main goal in this section is to derive a solution method for equations.
Bernoulli’s differential equation Yawin
A differential equation can be identified as a first order linear differential equation using its standard form: It is useful to have the coefficient of y be equal to 1. Our main goal in this section is to derive a solution method for equations of this form. The standard form of a linear differential equation is dy/dx + py =.
Mathematics Class 12 NCERT Solutions Chapter 9 Differential Equations
A differential equation can be identified as a first order linear differential equation using its standard form: The standard form of a linear differential equation is dy/dx + py = q, and it contains the variable y, and its derivatives. It is useful to have the coefficient of y be equal to 1. Our main goal in this section is.
Solved Write the differential equation e^x y' + e^2x y = sin
The standard form of a linear differential equation is dy/dx + py = q, and it contains the variable y, and its derivatives. It is useful to have the coefficient of y be equal to 1. A differential equation can be identified as a first order linear differential equation using its standard form: Our main goal in this section is.
Differential Equations Definition, Formula, Types, Examples
The standard form of a linear differential equation is dy/dx + py = q, and it contains the variable y, and its derivatives. Our main goal in this section is to derive a solution method for equations of this form. The p and q in this. It is useful to have the coefficient of y be equal to 1. A.
The standard form a linear differential equation Lesson1 YouTube
A differential equation can be identified as a first order linear differential equation using its standard form: The standard form of a linear differential equation is dy/dx + py = q, and it contains the variable y, and its derivatives. The p and q in this. It is useful to have the coefficient of y be equal to 1. Our.
Solved Express each of the differential equations in the
The p and q in this. A differential equation can be identified as a first order linear differential equation using its standard form: Our main goal in this section is to derive a solution method for equations of this form. It is useful to have the coefficient of y be equal to 1. The standard form of a linear differential.
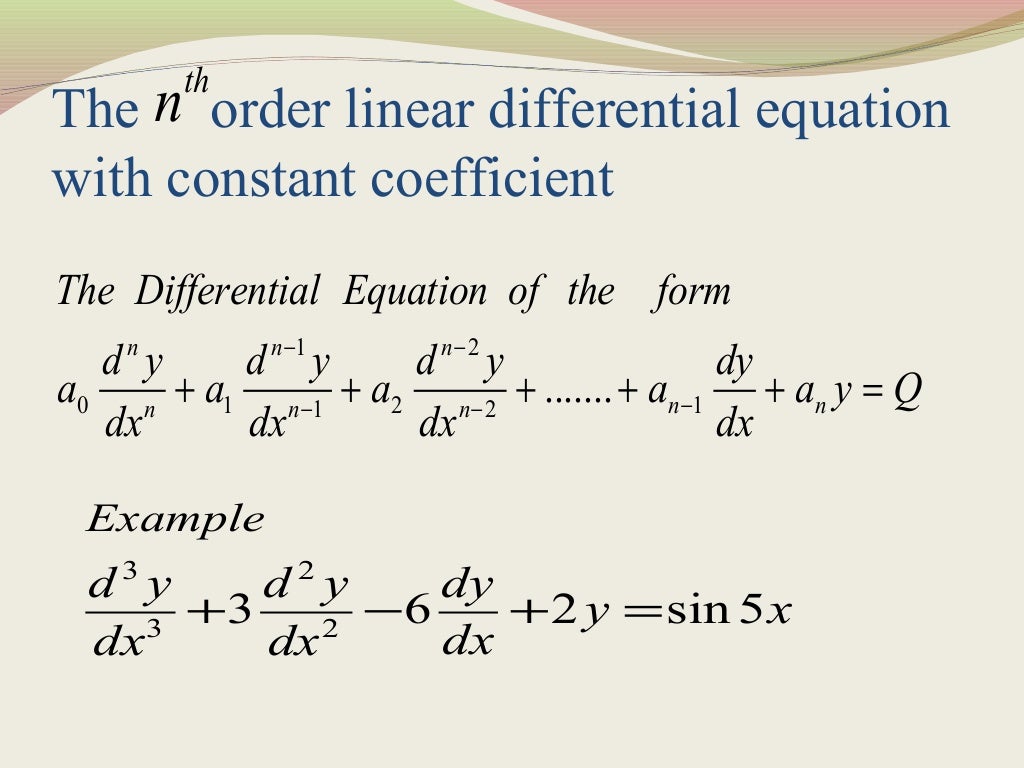
Linear differential equation with constant coefficient
A differential equation can be identified as a first order linear differential equation using its standard form: The standard form of a linear differential equation is dy/dx + py = q, and it contains the variable y, and its derivatives. It is useful to have the coefficient of y be equal to 1. The p and q in this. Our.
It Is Useful To Have The Coefficient Of Y Be Equal To 1.
The p and q in this. Our main goal in this section is to derive a solution method for equations of this form. The standard form of a linear differential equation is dy/dx + py = q, and it contains the variable y, and its derivatives. A differential equation can be identified as a first order linear differential equation using its standard form: