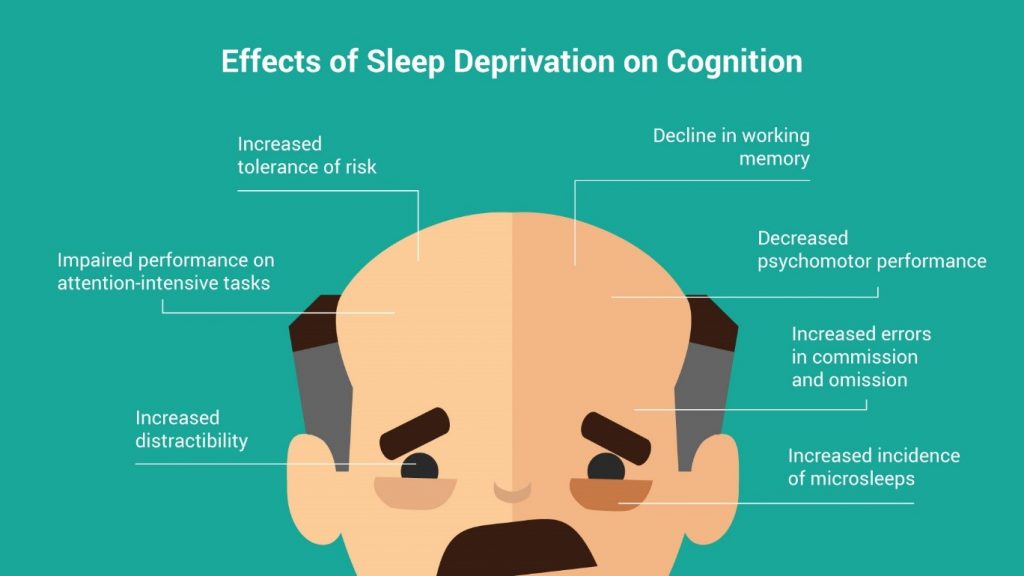
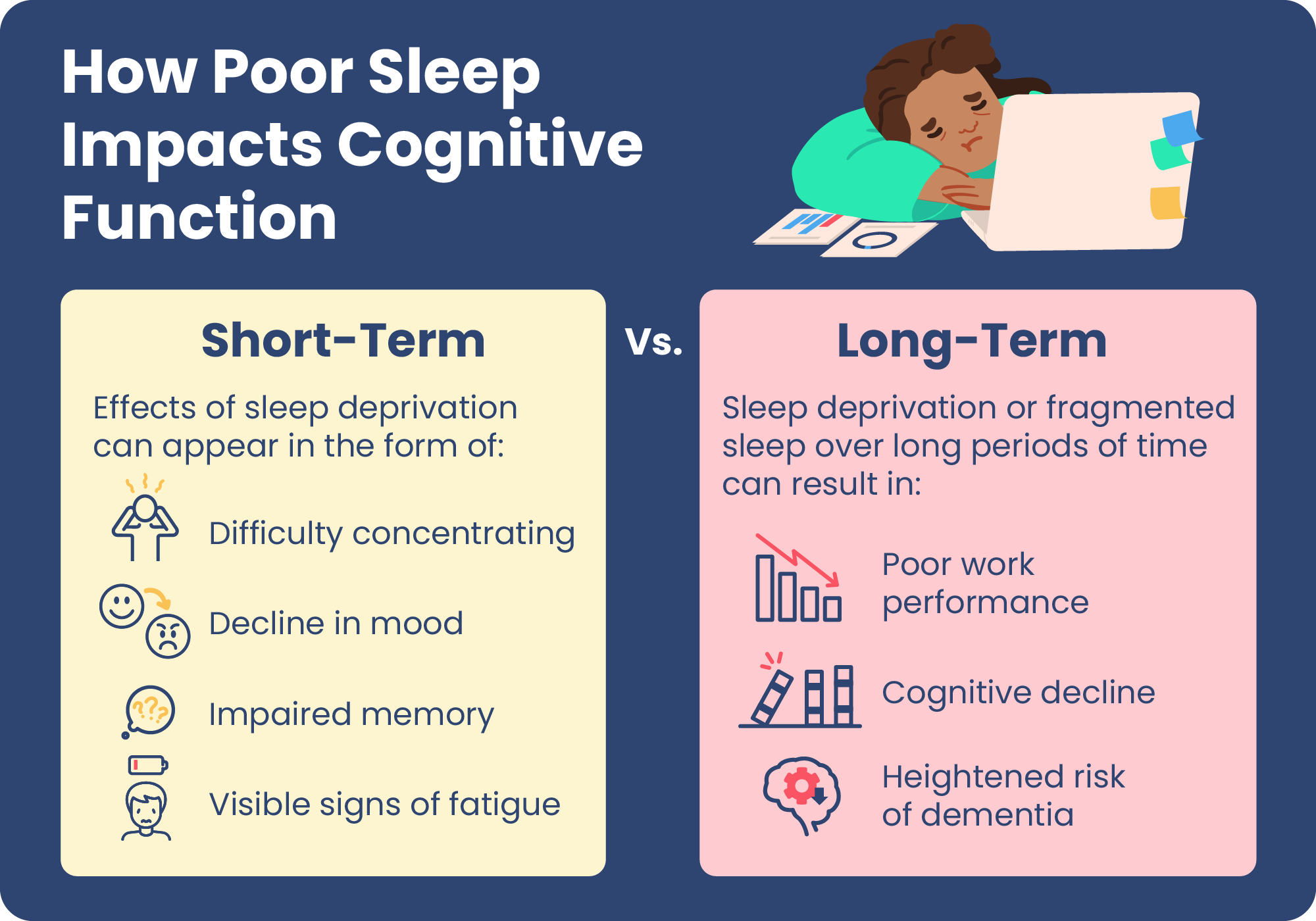
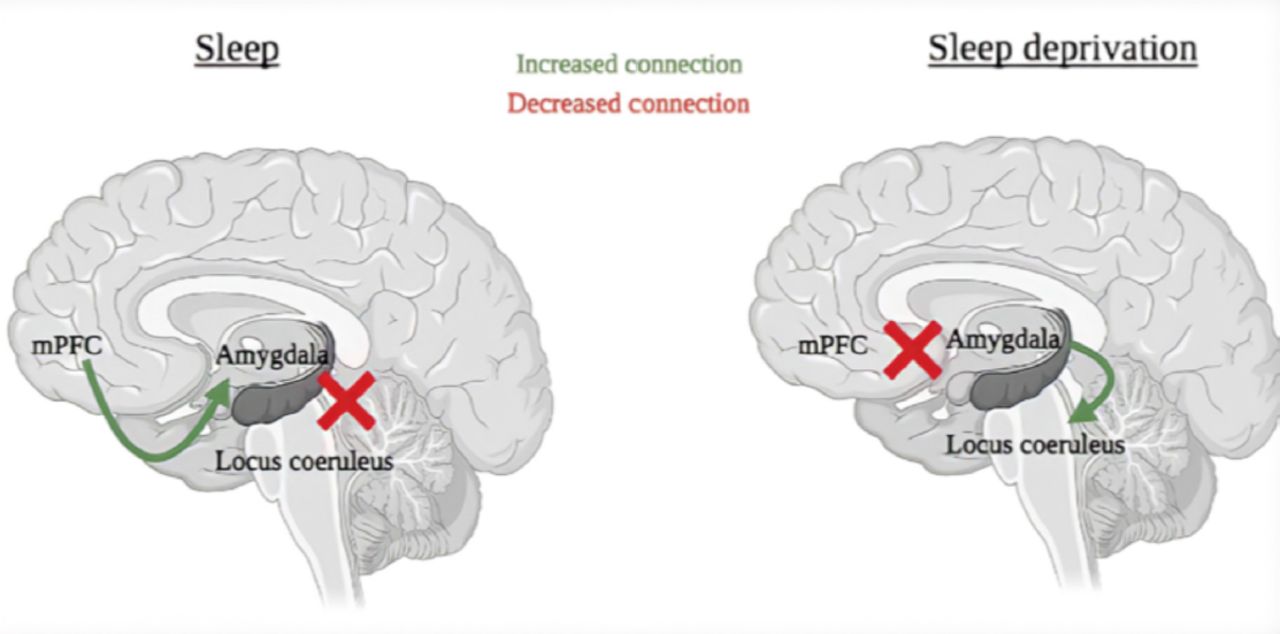
Sleep And Cognitive Performance
Sleep And Cognitive Performance - A lack of sleep, or sleep deprivation (sd), is a widespread phenomenon that can induce adverse changes in cognitive performance. In this article, we elaborate on how memory reactivation during sleep contributes to memory stability and memory use. Central to this debate has been the question of whether sleep deprivation affects nearly all cognitive capacities in a global manner through.
A lack of sleep, or sleep deprivation (sd), is a widespread phenomenon that can induce adverse changes in cognitive performance. In this article, we elaborate on how memory reactivation during sleep contributes to memory stability and memory use. Central to this debate has been the question of whether sleep deprivation affects nearly all cognitive capacities in a global manner through.
In this article, we elaborate on how memory reactivation during sleep contributes to memory stability and memory use. Central to this debate has been the question of whether sleep deprivation affects nearly all cognitive capacities in a global manner through. A lack of sleep, or sleep deprivation (sd), is a widespread phenomenon that can induce adverse changes in cognitive performance.
How to Sleep Better for Improved Cognitive Performance Viral Rang
In this article, we elaborate on how memory reactivation during sleep contributes to memory stability and memory use. Central to this debate has been the question of whether sleep deprivation affects nearly all cognitive capacities in a global manner through. A lack of sleep, or sleep deprivation (sd), is a widespread phenomenon that can induce adverse changes in cognitive performance.
The Role of Sleep Quality in Cognitive Performance Psychology Reads
In this article, we elaborate on how memory reactivation during sleep contributes to memory stability and memory use. Central to this debate has been the question of whether sleep deprivation affects nearly all cognitive capacities in a global manner through. A lack of sleep, or sleep deprivation (sd), is a widespread phenomenon that can induce adverse changes in cognitive performance.
Sleep Features Predict Cognitive Performance in Older Adults
Central to this debate has been the question of whether sleep deprivation affects nearly all cognitive capacities in a global manner through. A lack of sleep, or sleep deprivation (sd), is a widespread phenomenon that can induce adverse changes in cognitive performance. In this article, we elaborate on how memory reactivation during sleep contributes to memory stability and memory use.
Sleep Deprivation Its Effects On The Cognitive Preformance Sushant
In this article, we elaborate on how memory reactivation during sleep contributes to memory stability and memory use. A lack of sleep, or sleep deprivation (sd), is a widespread phenomenon that can induce adverse changes in cognitive performance. Central to this debate has been the question of whether sleep deprivation affects nearly all cognitive capacities in a global manner through.
Four Major Sleep Related Factors That Affect Our Cognitive Performance
A lack of sleep, or sleep deprivation (sd), is a widespread phenomenon that can induce adverse changes in cognitive performance. In this article, we elaborate on how memory reactivation during sleep contributes to memory stability and memory use. Central to this debate has been the question of whether sleep deprivation affects nearly all cognitive capacities in a global manner through.
How Does Lack of Sleep Affect Cognitive Impairment? Sleep Foundation
Central to this debate has been the question of whether sleep deprivation affects nearly all cognitive capacities in a global manner through. In this article, we elaborate on how memory reactivation during sleep contributes to memory stability and memory use. A lack of sleep, or sleep deprivation (sd), is a widespread phenomenon that can induce adverse changes in cognitive performance.
The Relationship Between Sleep and Cognitive Functioning The QLD MIND
Central to this debate has been the question of whether sleep deprivation affects nearly all cognitive capacities in a global manner through. In this article, we elaborate on how memory reactivation during sleep contributes to memory stability and memory use. A lack of sleep, or sleep deprivation (sd), is a widespread phenomenon that can induce adverse changes in cognitive performance.
The consequences of sleep deprivation on cognitive performance
In this article, we elaborate on how memory reactivation during sleep contributes to memory stability and memory use. Central to this debate has been the question of whether sleep deprivation affects nearly all cognitive capacities in a global manner through. A lack of sleep, or sleep deprivation (sd), is a widespread phenomenon that can induce adverse changes in cognitive performance.
Graphic summary of main findings in sleep and cognitive performance
A lack of sleep, or sleep deprivation (sd), is a widespread phenomenon that can induce adverse changes in cognitive performance. Central to this debate has been the question of whether sleep deprivation affects nearly all cognitive capacities in a global manner through. In this article, we elaborate on how memory reactivation during sleep contributes to memory stability and memory use.
Relationship of quality of sleep with cognitive performance and
In this article, we elaborate on how memory reactivation during sleep contributes to memory stability and memory use. Central to this debate has been the question of whether sleep deprivation affects nearly all cognitive capacities in a global manner through. A lack of sleep, or sleep deprivation (sd), is a widespread phenomenon that can induce adverse changes in cognitive performance.
In This Article, We Elaborate On How Memory Reactivation During Sleep Contributes To Memory Stability And Memory Use.
Central to this debate has been the question of whether sleep deprivation affects nearly all cognitive capacities in a global manner through. A lack of sleep, or sleep deprivation (sd), is a widespread phenomenon that can induce adverse changes in cognitive performance.