Ovulated Oocyte
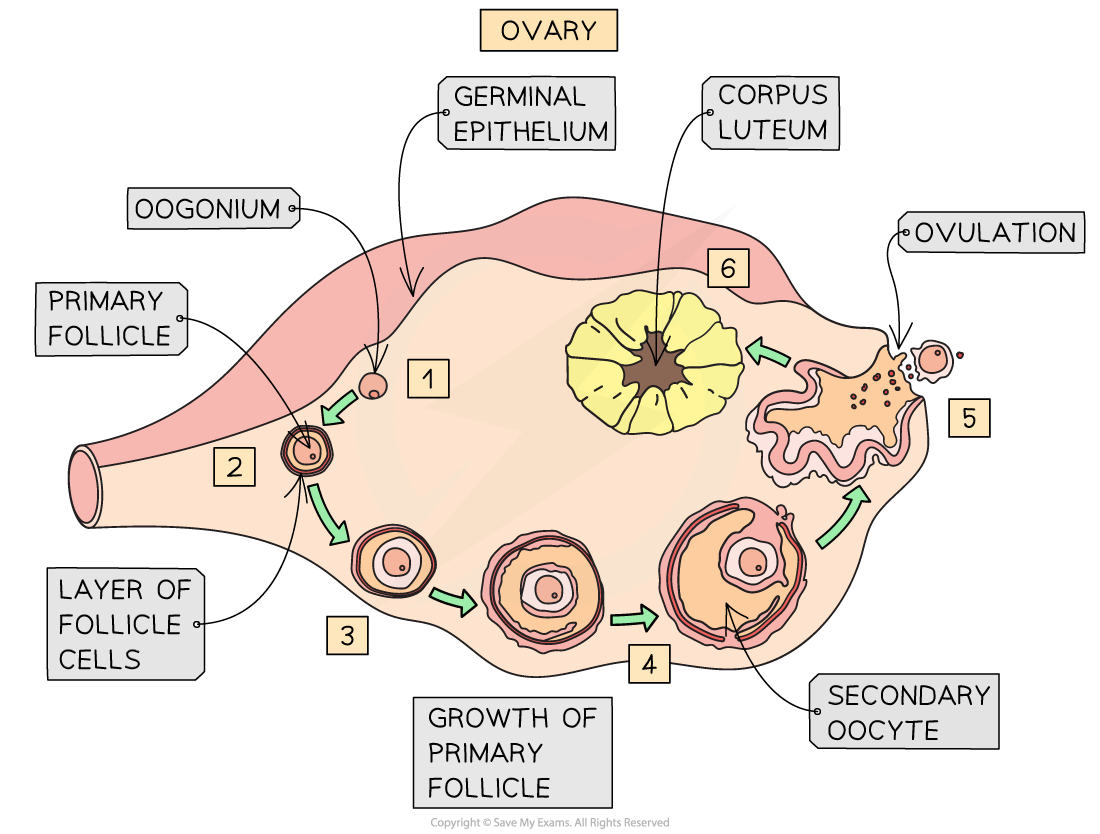
Ovulated Oocyte - The oocyte is ovulated at the mii stage. Ovulation of an oocyte from the ovary into the oviduct for fertilization is a tightly regulated process, engaging multiple physiological. Sister chromatids will be segregated after fertilization. During oogenesis, the oogonia become primary oocytes. An oocyte is a form of genetic material that can be collected for cryoconservation. In humans generally a single oocyte is released from a cohort of several maturing.
Ovulation of an oocyte from the ovary into the oviduct for fertilization is a tightly regulated process, engaging multiple physiological. An oocyte is a form of genetic material that can be collected for cryoconservation. The oocyte is ovulated at the mii stage. Sister chromatids will be segregated after fertilization. During oogenesis, the oogonia become primary oocytes. In humans generally a single oocyte is released from a cohort of several maturing.
In humans generally a single oocyte is released from a cohort of several maturing. The oocyte is ovulated at the mii stage. During oogenesis, the oogonia become primary oocytes. Ovulation of an oocyte from the ovary into the oviduct for fertilization is a tightly regulated process, engaging multiple physiological. Sister chromatids will be segregated after fertilization. An oocyte is a form of genetic material that can be collected for cryoconservation.
Explain the development of a secondary oocyte (ovu
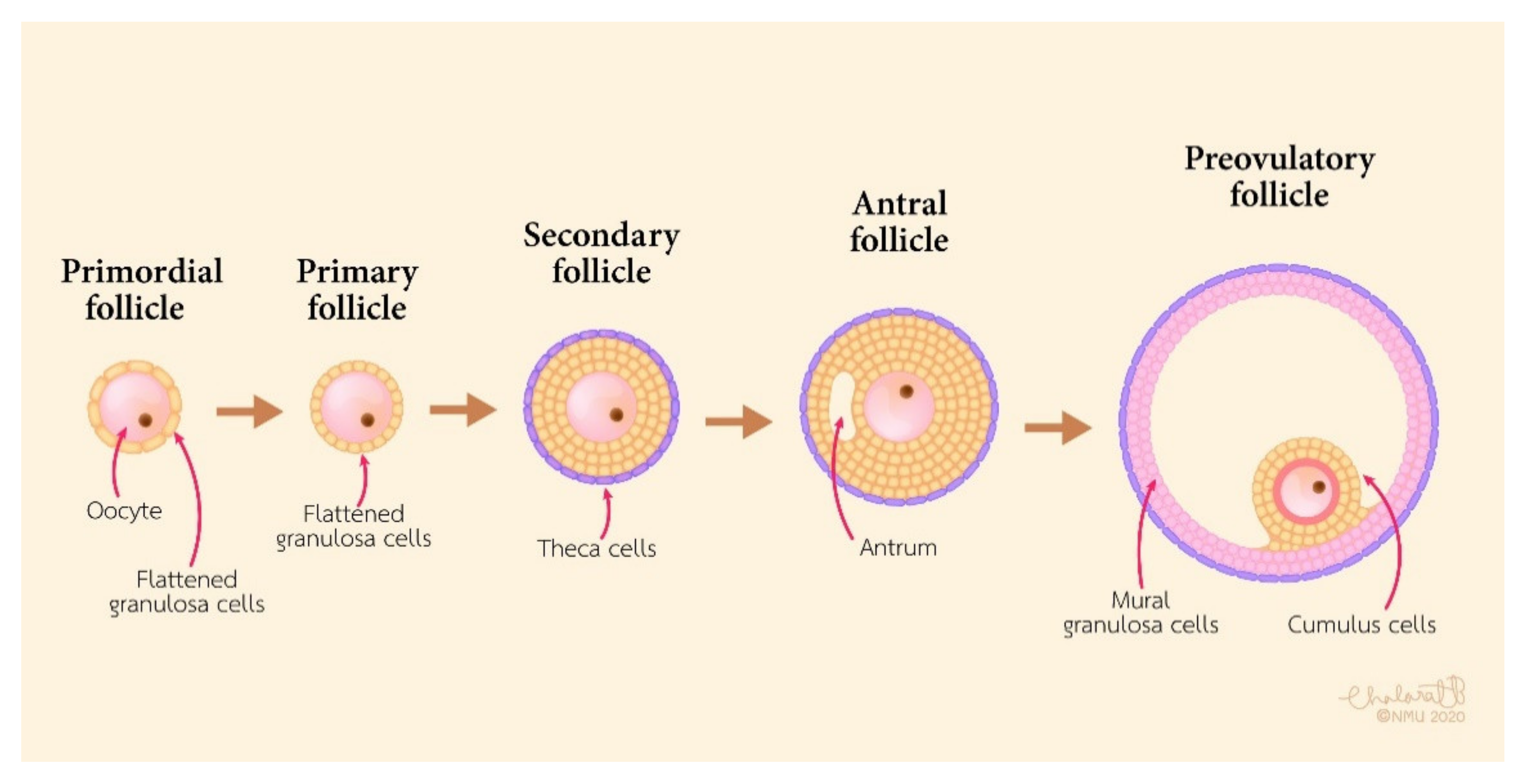
In humans generally a single oocyte is released from a cohort of several maturing. Sister chromatids will be segregated after fertilization. The oocyte is ovulated at the mii stage. Ovulation of an oocyte from the ovary into the oviduct for fertilization is a tightly regulated process, engaging multiple physiological. An oocyte is a form of genetic material that can be.
Chapter 29 Oocyte at ovulation Diagram Quizlet
Ovulation of an oocyte from the ovary into the oviduct for fertilization is a tightly regulated process, engaging multiple physiological. An oocyte is a form of genetic material that can be collected for cryoconservation. Sister chromatids will be segregated after fertilization. In humans generally a single oocyte is released from a cohort of several maturing. The oocyte is ovulated at.
Human Pregnancy and Birth · Biology
Ovulation of an oocyte from the ovary into the oviduct for fertilization is a tightly regulated process, engaging multiple physiological. The oocyte is ovulated at the mii stage. An oocyte is a form of genetic material that can be collected for cryoconservation. Sister chromatids will be segregated after fertilization. In humans generally a single oocyte is released from a cohort.
What is Oogenesis? Definition, Stages, Process Tutoroot
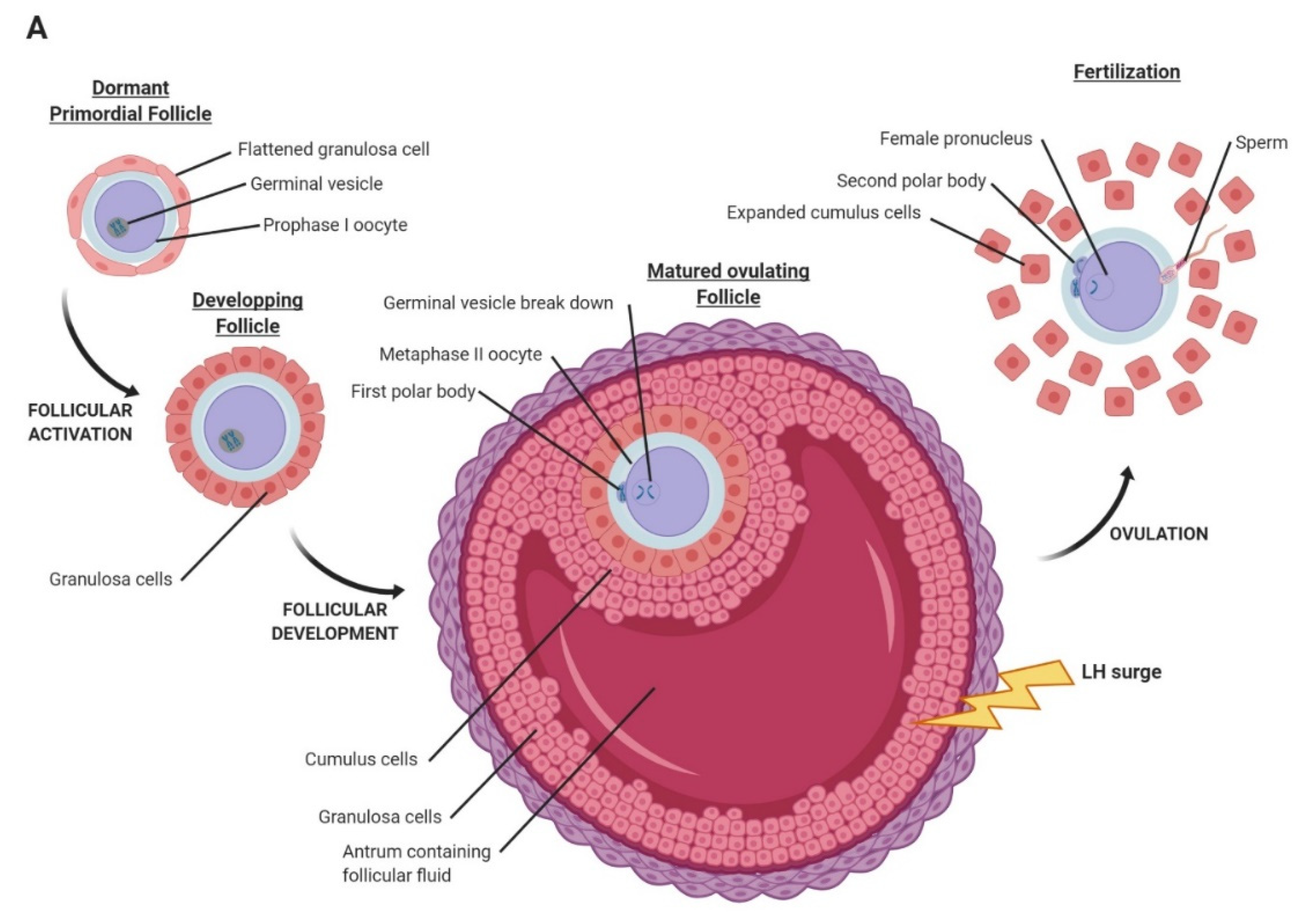
Ovulation of an oocyte from the ovary into the oviduct for fertilization is a tightly regulated process, engaging multiple physiological. In humans generally a single oocyte is released from a cohort of several maturing. The oocyte is ovulated at the mii stage. An oocyte is a form of genetic material that can be collected for cryoconservation. During oogenesis, the oogonia.
Fallopian Tube The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
Sister chromatids will be segregated after fertilization. During oogenesis, the oogonia become primary oocytes. An oocyte is a form of genetic material that can be collected for cryoconservation. Ovulation of an oocyte from the ovary into the oviduct for fertilization is a tightly regulated process, engaging multiple physiological. In humans generally a single oocyte is released from a cohort of.
Maturation
In humans generally a single oocyte is released from a cohort of several maturing. Sister chromatids will be segregated after fertilization. Ovulation of an oocyte from the ovary into the oviduct for fertilization is a tightly regulated process, engaging multiple physiological. During oogenesis, the oogonia become primary oocytes. An oocyte is a form of genetic material that can be collected.
A Ovulated oocytes from in vitro cultured HA encapsulated preantral
Sister chromatids will be segregated after fertilization. In humans generally a single oocyte is released from a cohort of several maturing. During oogenesis, the oogonia become primary oocytes. Ovulation of an oocyte from the ovary into the oviduct for fertilization is a tightly regulated process, engaging multiple physiological. An oocyte is a form of genetic material that can be collected.
The Function of Cumulus Cells in Oocyte Growth and Maturation and in
Ovulation of an oocyte from the ovary into the oviduct for fertilization is a tightly regulated process, engaging multiple physiological. An oocyte is a form of genetic material that can be collected for cryoconservation. During oogenesis, the oogonia become primary oocytes. The oocyte is ovulated at the mii stage. In humans generally a single oocyte is released from a cohort.
Oocyte (Ovulation and Fertilization) Diagram Quizlet
Ovulation of an oocyte from the ovary into the oviduct for fertilization is a tightly regulated process, engaging multiple physiological. The oocyte is ovulated at the mii stage. During oogenesis, the oogonia become primary oocytes. An oocyte is a form of genetic material that can be collected for cryoconservation. Sister chromatids will be segregated after fertilization.
IJMS Free FullText Adipokines Expression and Effects in Oocyte
In humans generally a single oocyte is released from a cohort of several maturing. Sister chromatids will be segregated after fertilization. The oocyte is ovulated at the mii stage. Ovulation of an oocyte from the ovary into the oviduct for fertilization is a tightly regulated process, engaging multiple physiological. An oocyte is a form of genetic material that can be.
An Oocyte Is A Form Of Genetic Material That Can Be Collected For Cryoconservation.
During oogenesis, the oogonia become primary oocytes. Ovulation of an oocyte from the ovary into the oviduct for fertilization is a tightly regulated process, engaging multiple physiological. In humans generally a single oocyte is released from a cohort of several maturing. Sister chromatids will be segregated after fertilization.