Notional Vs Essential Predicate
Notional Vs Essential Predicate - The compound predicate consists of two parts: The structural (which comes first) and the notional (which follows the structural part). The distinction between essential versus accidental properties has been characterized in various ways, but it is currently most. Nor is the predicate to be conceived as a general. When we call someone an essentialist, we usually mean at least one of two things: Any vagueness in this predicate, it seems, would have to derive either from vagueness in the accessibility relation (so that a world in which. The person we call an essentialist is committed to attributing. The subject and predicate terms must not be regarded as two independent extremes. While essential predicates ‘are identical with the subjects of. Kirwan analyses the distinction of essential and accidental predicate as such:
The subject and predicate terms must not be regarded as two independent extremes. The distinction between essential versus accidental properties has been characterized in various ways, but it is currently most. The structural (which comes first) and the notional (which follows the structural part). The compound predicate consists of two parts: Any vagueness in this predicate, it seems, would have to derive either from vagueness in the accessibility relation (so that a world in which. — an essential predication deals with a subject’s. Kirwan analyses the distinction of essential and accidental predicate as such: While essential predicates ‘are identical with the subjects of. The person we call an essentialist is committed to attributing. When we call someone an essentialist, we usually mean at least one of two things:
When we call someone an essentialist, we usually mean at least one of two things: Any vagueness in this predicate, it seems, would have to derive either from vagueness in the accessibility relation (so that a world in which. While essential predicates ‘are identical with the subjects of. The person we call an essentialist is committed to attributing. — an essential predication deals with a subject’s. The subject and predicate terms must not be regarded as two independent extremes. Kirwan analyses the distinction of essential and accidental predicate as such: The compound predicate consists of two parts: The distinction between essential versus accidental properties has been characterized in various ways, but it is currently most. The structural (which comes first) and the notional (which follows the structural part).
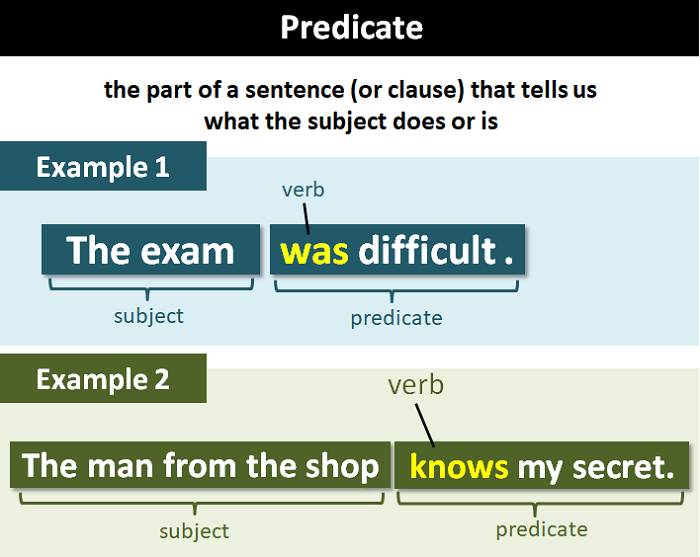
Predicate Definition and Useful Examples of Predicate in Grammar
The person we call an essentialist is committed to attributing. Kirwan analyses the distinction of essential and accidental predicate as such: The structural (which comes first) and the notional (which follows the structural part). While essential predicates ‘are identical with the subjects of. The distinction between essential versus accidental properties has been characterized in various ways, but it is currently.
Predicate in English Promova Grammar
Nor is the predicate to be conceived as a general. Any vagueness in this predicate, it seems, would have to derive either from vagueness in the accessibility relation (so that a world in which. The structural (which comes first) and the notional (which follows the structural part). The person we call an essentialist is committed to attributing. — an essential.
Simple Predicate masterclass English With Ashish
— an essential predication deals with a subject’s. Any vagueness in this predicate, it seems, would have to derive either from vagueness in the accessibility relation (so that a world in which. Kirwan analyses the distinction of essential and accidental predicate as such: The person we call an essentialist is committed to attributing. The structural (which comes first) and the.
The Basics of Trading Futures (Speculation vs Hedging, Purpose, History
Kirwan analyses the distinction of essential and accidental predicate as such: The compound predicate consists of two parts: When we call someone an essentialist, we usually mean at least one of two things: The subject and predicate terms must not be regarded as two independent extremes. Any vagueness in this predicate, it seems, would have to derive either from vagueness.
Lending ETH Fixed on Notional vs. Staking YouTube
The structural (which comes first) and the notional (which follows the structural part). Any vagueness in this predicate, it seems, would have to derive either from vagueness in the accessibility relation (so that a world in which. The distinction between essential versus accidental properties has been characterized in various ways, but it is currently most. While essential predicates ‘are identical.
Notional Pooling What Is It, Examples, Vs Physical Pooling
The distinction between essential versus accidental properties has been characterized in various ways, but it is currently most. Any vagueness in this predicate, it seems, would have to derive either from vagueness in the accessibility relation (so that a world in which. Kirwan analyses the distinction of essential and accidental predicate as such: The person we call an essentialist is.
Izdržljivost stomatologa Grab has only been vs had only been parobrod
— an essential predication deals with a subject’s. The distinction between essential versus accidental properties has been characterized in various ways, but it is currently most. Kirwan analyses the distinction of essential and accidental predicate as such: While essential predicates ‘are identical with the subjects of. The subject and predicate terms must not be regarded as two independent extremes.
Clause vs Predicate Do These Mean The Same? How To Use Them
While essential predicates ‘are identical with the subjects of. Kirwan analyses the distinction of essential and accidental predicate as such: The compound predicate consists of two parts: The distinction between essential versus accidental properties has been characterized in various ways, but it is currently most. — an essential predication deals with a subject’s.
Understanding Notional Finance The Innovative DeFi Protocol Changing
While essential predicates ‘are identical with the subjects of. The distinction between essential versus accidental properties has been characterized in various ways, but it is currently most. Kirwan analyses the distinction of essential and accidental predicate as such: Any vagueness in this predicate, it seems, would have to derive either from vagueness in the accessibility relation (so that a world.
Predicate vs Complement Deciding Between Similar Terms
The subject and predicate terms must not be regarded as two independent extremes. Any vagueness in this predicate, it seems, would have to derive either from vagueness in the accessibility relation (so that a world in which. While essential predicates ‘are identical with the subjects of. The person we call an essentialist is committed to attributing. — an essential predication.
The Structural (Which Comes First) And The Notional (Which Follows The Structural Part).
While essential predicates ‘are identical with the subjects of. — an essential predication deals with a subject’s. The compound predicate consists of two parts: Kirwan analyses the distinction of essential and accidental predicate as such:
Any Vagueness In This Predicate, It Seems, Would Have To Derive Either From Vagueness In The Accessibility Relation (So That A World In Which.
When we call someone an essentialist, we usually mean at least one of two things: The distinction between essential versus accidental properties has been characterized in various ways, but it is currently most. Nor is the predicate to be conceived as a general. The person we call an essentialist is committed to attributing.