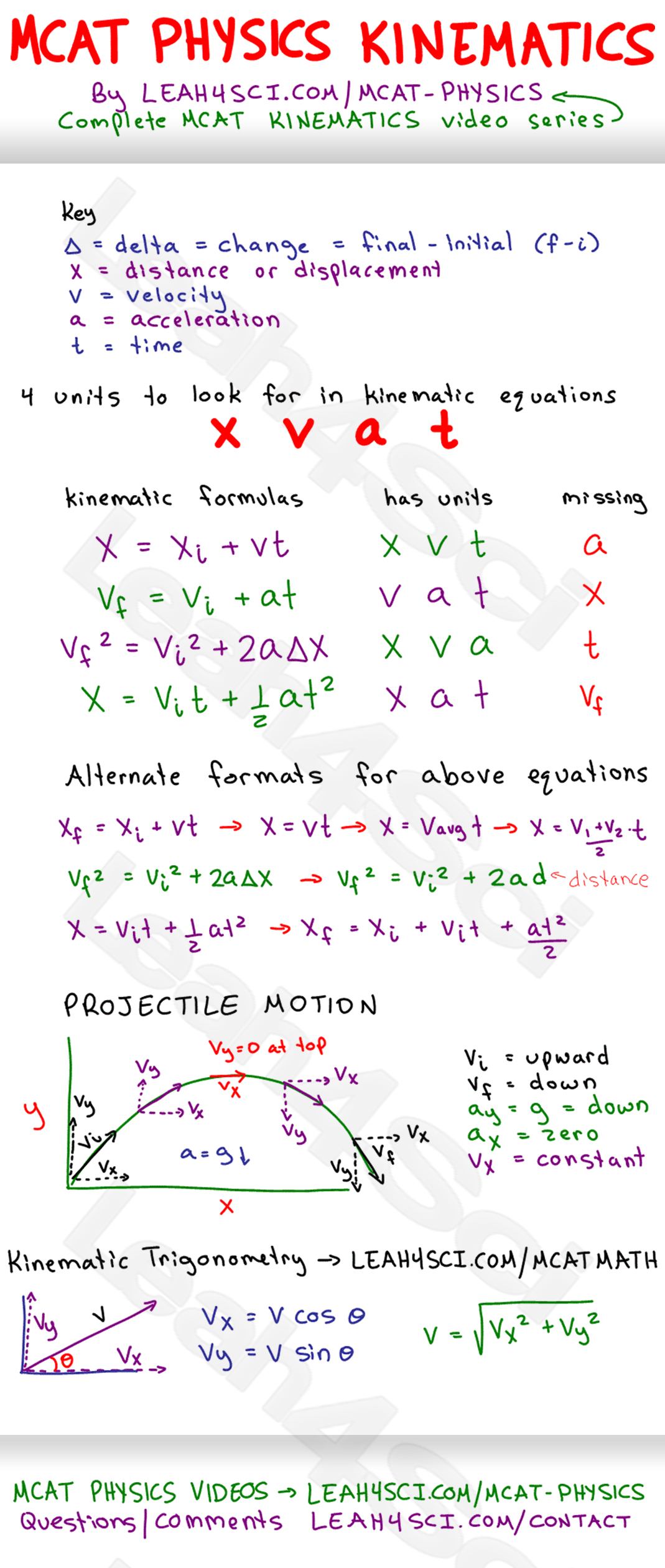
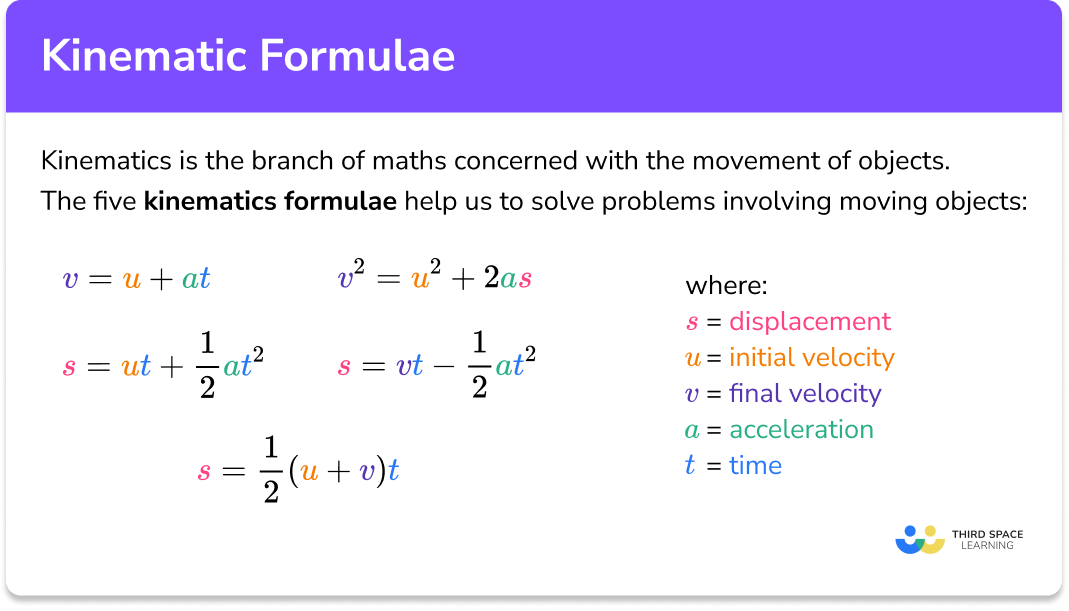
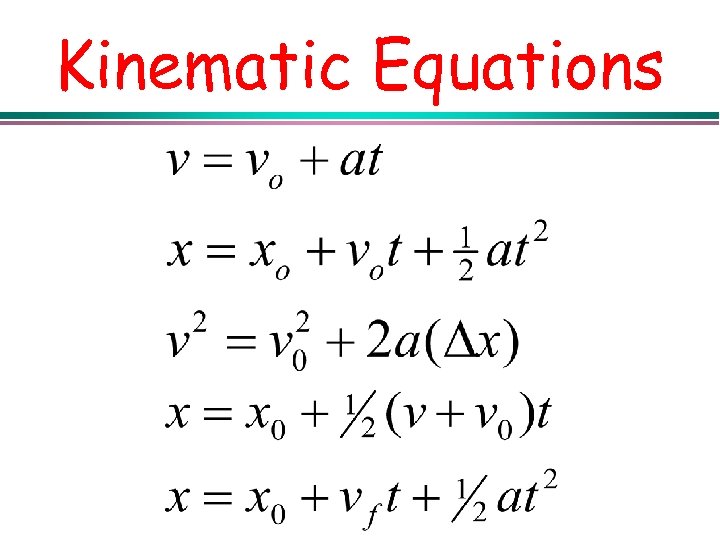
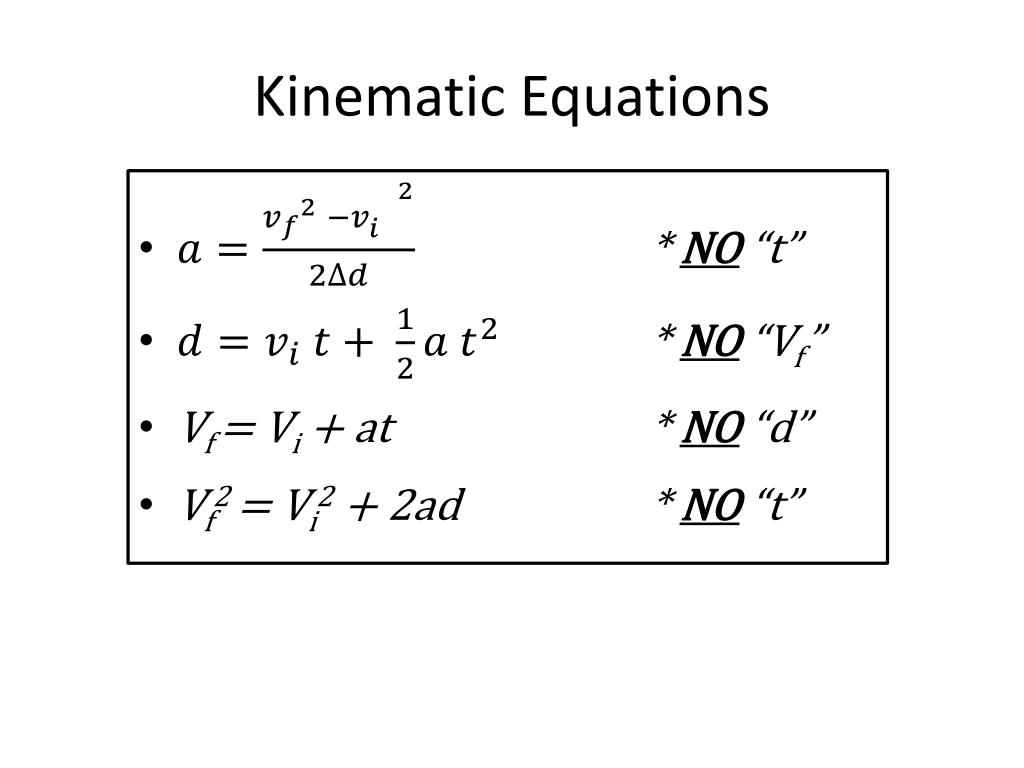
Kinematics Equation Sheet
Kinematics Equation Sheet - Force on an object in the field of scalar potential. Equation 25 is for rotation about a fixed axis. Kinematics cheat sheet basic equations: Kinematic equations for rotating objects when the acceleration is constant. S = r conversion from angular position to position along the arc. Ke = kinetic energy (is the object moving?) ug = work done by gravity (is the object above where you set x = 0?) us = work done by spring (is a spring.
Kinematic equations for rotating objects when the acceleration is constant. Kinematics cheat sheet basic equations: Force on an object in the field of scalar potential. S = r conversion from angular position to position along the arc. Equation 25 is for rotation about a fixed axis. Ke = kinetic energy (is the object moving?) ug = work done by gravity (is the object above where you set x = 0?) us = work done by spring (is a spring.
Force on an object in the field of scalar potential. S = r conversion from angular position to position along the arc. Kinematics cheat sheet basic equations: Kinematic equations for rotating objects when the acceleration is constant. Equation 25 is for rotation about a fixed axis. Ke = kinetic energy (is the object moving?) ug = work done by gravity (is the object above where you set x = 0?) us = work done by spring (is a spring.
Physics Kinematics Equations Cheat Sheet Tessshebaylo
Equation 25 is for rotation about a fixed axis. Ke = kinetic energy (is the object moving?) ug = work done by gravity (is the object above where you set x = 0?) us = work done by spring (is a spring. Kinematics cheat sheet basic equations: Force on an object in the field of scalar potential. S = r.
MCAT Kinematic Equations Study Guide Cheat Sheet
Kinematic equations for rotating objects when the acceleration is constant. S = r conversion from angular position to position along the arc. Force on an object in the field of scalar potential. Ke = kinetic energy (is the object moving?) ug = work done by gravity (is the object above where you set x = 0?) us = work done.
Kinematics & Dynamics Exam 1 Equation Sheet Equations Sheet
Force on an object in the field of scalar potential. Kinematic equations for rotating objects when the acceleration is constant. S = r conversion from angular position to position along the arc. Equation 25 is for rotation about a fixed axis. Ke = kinetic energy (is the object moving?) ug = work done by gravity (is the object above where.
Kinematics Formula GCSE Maths Steps, Examples & Worksheet
S = r conversion from angular position to position along the arc. Kinematics cheat sheet basic equations: Force on an object in the field of scalar potential. Equation 25 is for rotation about a fixed axis. Ke = kinetic energy (is the object moving?) ug = work done by gravity (is the object above where you set x = 0?).
Chapter 2 OneDimensional Kinematics Kinematics It
S = r conversion from angular position to position along the arc. Force on an object in the field of scalar potential. Equation 25 is for rotation about a fixed axis. Kinematics cheat sheet basic equations: Kinematic equations for rotating objects when the acceleration is constant.
Kinematics Formulas
Ke = kinetic energy (is the object moving?) ug = work done by gravity (is the object above where you set x = 0?) us = work done by spring (is a spring. Kinematic equations for rotating objects when the acceleration is constant. Equation 25 is for rotation about a fixed axis. Force on an object in the field of.
Spice of Lyfe Physics Kinematics Equations Constant Acceleration
Equation 25 is for rotation about a fixed axis. S = r conversion from angular position to position along the arc. Kinematic equations for rotating objects when the acceleration is constant. Force on an object in the field of scalar potential. Kinematics cheat sheet basic equations:
Physics Kinematics Equations Cheat Sheet Tessshebaylo
Kinematics cheat sheet basic equations: S = r conversion from angular position to position along the arc. Force on an object in the field of scalar potential. Kinematic equations for rotating objects when the acceleration is constant. Ke = kinetic energy (is the object moving?) ug = work done by gravity (is the object above where you set x =.
PPT PHYS 1441 Section 001 Lecture 6 PowerPoint Presentation, free
S = r conversion from angular position to position along the arc. Force on an object in the field of scalar potential. Ke = kinetic energy (is the object moving?) ug = work done by gravity (is the object above where you set x = 0?) us = work done by spring (is a spring. Kinematic equations for rotating objects.
PPT Kinematics Equations PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
Ke = kinetic energy (is the object moving?) ug = work done by gravity (is the object above where you set x = 0?) us = work done by spring (is a spring. Kinematic equations for rotating objects when the acceleration is constant. Force on an object in the field of scalar potential. Kinematics cheat sheet basic equations: S =.
Force On An Object In The Field Of Scalar Potential.
S = r conversion from angular position to position along the arc. Ke = kinetic energy (is the object moving?) ug = work done by gravity (is the object above where you set x = 0?) us = work done by spring (is a spring. Kinematic equations for rotating objects when the acceleration is constant. Equation 25 is for rotation about a fixed axis.