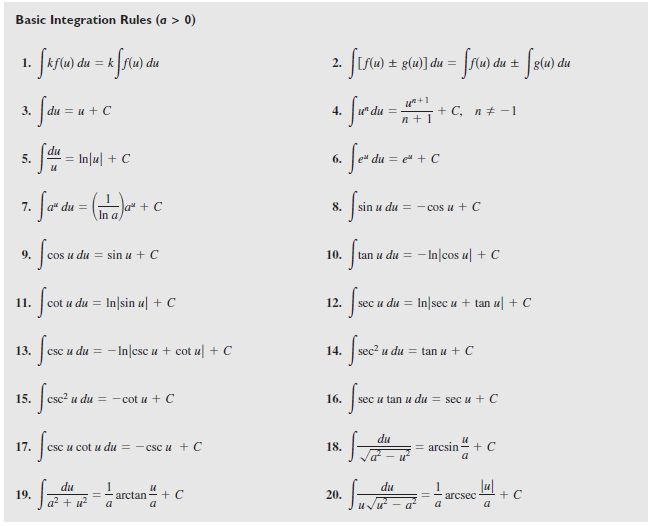
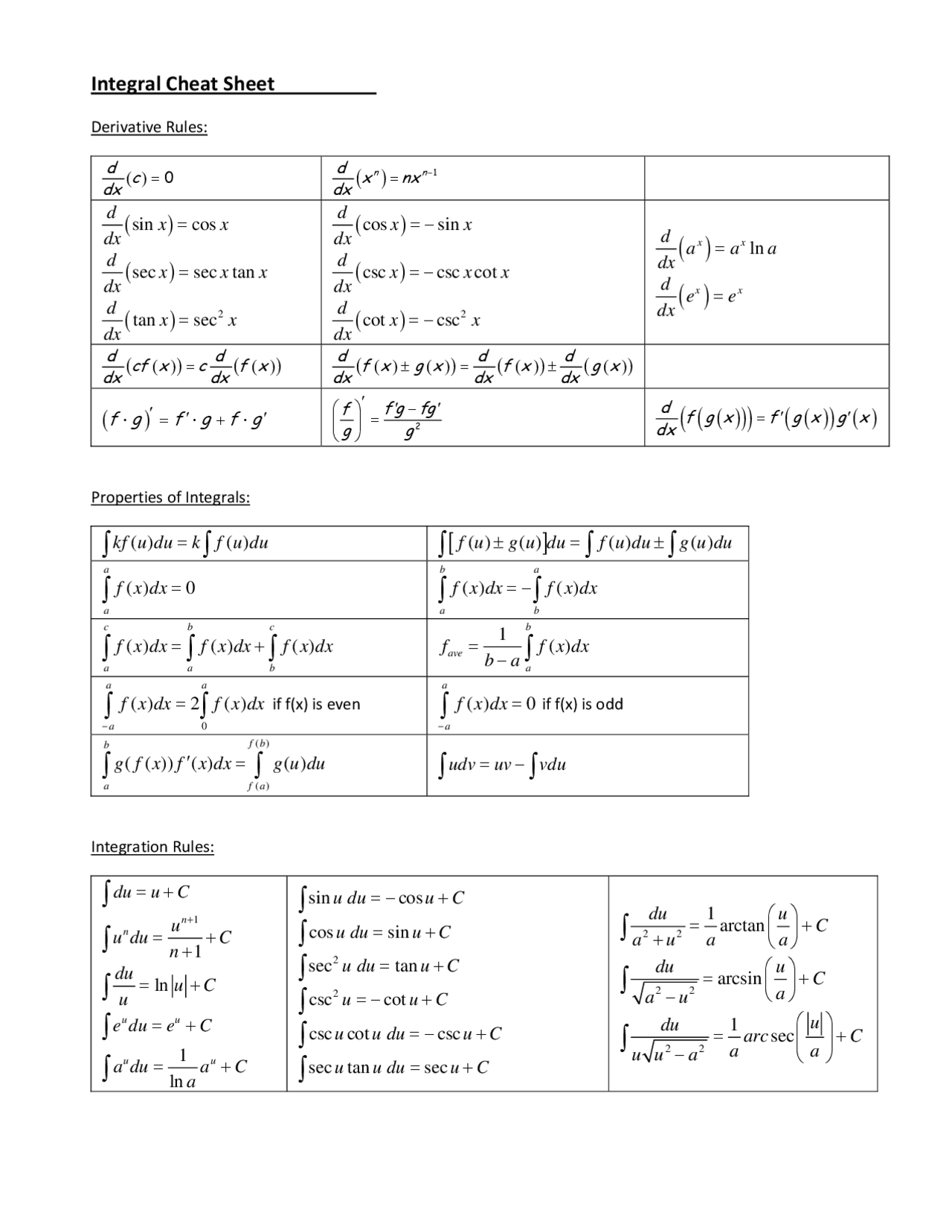
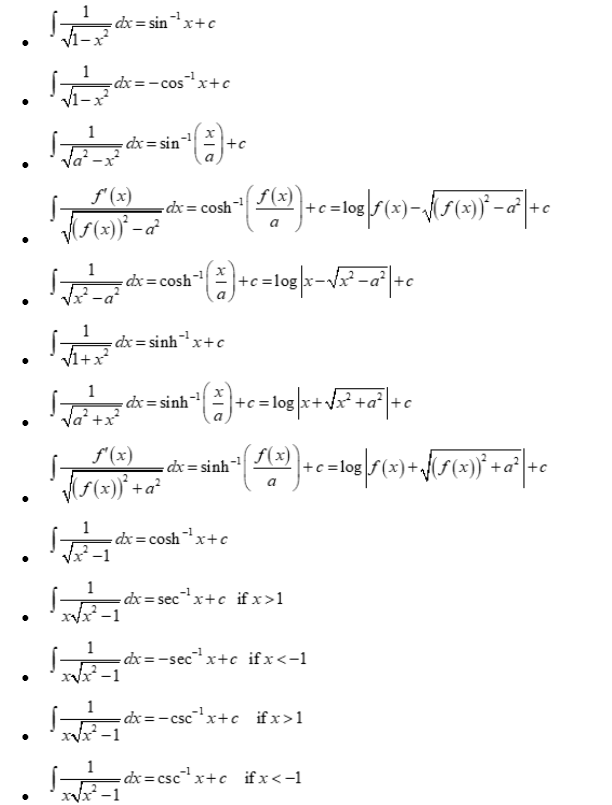Integral Rules Sheet
Integral Rules Sheet - ′= −∫ ′ ∫integral of a constant: Cheat sheet for integrals 1. Integral of a constant \int f\left(a\right)dx=x\cdot f\left(a\right) take the constant out \int a\cdot f\left(x\right)dx=a\cdot \int f\left(x\right)dx. ( ) 𝑥=𝑥⋅ ( ) ∫taking a constant out: Integral is called convergent if the limit exists and has a finite value and divergent if the limit doesn’t exist or has infinite value. ⋅ (𝑥 ) 𝑥= ⋅∫ 𝑥 𝑥 ∫sum/difference. Integrals with trigonometric functions z sinaxdx= 1 a cosax (63) z sin2 axdx= x 2 sin2ax 4a (64) z sinn axdx= 1 a cosax 2f 1 1 2;
Integrals with trigonometric functions z sinaxdx= 1 a cosax (63) z sin2 axdx= x 2 sin2ax 4a (64) z sinn axdx= 1 a cosax 2f 1 1 2; Integral is called convergent if the limit exists and has a finite value and divergent if the limit doesn’t exist or has infinite value. Integral of a constant \int f\left(a\right)dx=x\cdot f\left(a\right) take the constant out \int a\cdot f\left(x\right)dx=a\cdot \int f\left(x\right)dx. ( ) 𝑥=𝑥⋅ ( ) ∫taking a constant out: ⋅ (𝑥 ) 𝑥= ⋅∫ 𝑥 𝑥 ∫sum/difference. Cheat sheet for integrals 1. ′= −∫ ′ ∫integral of a constant:
Integrals with trigonometric functions z sinaxdx= 1 a cosax (63) z sin2 axdx= x 2 sin2ax 4a (64) z sinn axdx= 1 a cosax 2f 1 1 2; ( ) 𝑥=𝑥⋅ ( ) ∫taking a constant out: ′= −∫ ′ ∫integral of a constant: Integral of a constant \int f\left(a\right)dx=x\cdot f\left(a\right) take the constant out \int a\cdot f\left(x\right)dx=a\cdot \int f\left(x\right)dx. ⋅ (𝑥 ) 𝑥= ⋅∫ 𝑥 𝑥 ∫sum/difference. Integral is called convergent if the limit exists and has a finite value and divergent if the limit doesn’t exist or has infinite value. Cheat sheet for integrals 1.
Basic Rules Of Integration
Integral is called convergent if the limit exists and has a finite value and divergent if the limit doesn’t exist or has infinite value. Integral of a constant \int f\left(a\right)dx=x\cdot f\left(a\right) take the constant out \int a\cdot f\left(x\right)dx=a\cdot \int f\left(x\right)dx. Cheat sheet for integrals 1. ′= −∫ ′ ∫integral of a constant: Integrals with trigonometric functions z sinaxdx= 1 a.
Basic Integral Formulas
( ) 𝑥=𝑥⋅ ( ) ∫taking a constant out: ⋅ (𝑥 ) 𝑥= ⋅∫ 𝑥 𝑥 ∫sum/difference. Integral of a constant \int f\left(a\right)dx=x\cdot f\left(a\right) take the constant out \int a\cdot f\left(x\right)dx=a\cdot \int f\left(x\right)dx. ′= −∫ ′ ∫integral of a constant: Integral is called convergent if the limit exists and has a finite value and divergent if the limit doesn’t exist.
Printable Integrals Table
Integral of a constant \int f\left(a\right)dx=x\cdot f\left(a\right) take the constant out \int a\cdot f\left(x\right)dx=a\cdot \int f\left(x\right)dx. ( ) 𝑥=𝑥⋅ ( ) ∫taking a constant out: Integral is called convergent if the limit exists and has a finite value and divergent if the limit doesn’t exist or has infinite value. Cheat sheet for integrals 1. ⋅ (𝑥 ) 𝑥= ⋅∫ 𝑥.
Basic Rules Of Integration
( ) 𝑥=𝑥⋅ ( ) ∫taking a constant out: Integrals with trigonometric functions z sinaxdx= 1 a cosax (63) z sin2 axdx= x 2 sin2ax 4a (64) z sinn axdx= 1 a cosax 2f 1 1 2; ⋅ (𝑥 ) 𝑥= ⋅∫ 𝑥 𝑥 ∫sum/difference. ′= −∫ ′ ∫integral of a constant: Cheat sheet for integrals 1.
Solved Determine which of the integrals can be found using
Integral of a constant \int f\left(a\right)dx=x\cdot f\left(a\right) take the constant out \int a\cdot f\left(x\right)dx=a\cdot \int f\left(x\right)dx. ′= −∫ ′ ∫integral of a constant: Integrals with trigonometric functions z sinaxdx= 1 a cosax (63) z sin2 axdx= x 2 sin2ax 4a (64) z sinn axdx= 1 a cosax 2f 1 1 2; ⋅ (𝑥 ) 𝑥= ⋅∫ 𝑥 𝑥 ∫sum/difference. Integral.
Basic Integral Rules
Cheat sheet for integrals 1. Integrals with trigonometric functions z sinaxdx= 1 a cosax (63) z sin2 axdx= x 2 sin2ax 4a (64) z sinn axdx= 1 a cosax 2f 1 1 2; ′= −∫ ′ ∫integral of a constant: ⋅ (𝑥 ) 𝑥= ⋅∫ 𝑥 𝑥 ∫sum/difference. ( ) 𝑥=𝑥⋅ ( ) ∫taking a constant out:
Integrals ONE GREAT WORLD FOR ALL
Integral of a constant \int f\left(a\right)dx=x\cdot f\left(a\right) take the constant out \int a\cdot f\left(x\right)dx=a\cdot \int f\left(x\right)dx. Integral is called convergent if the limit exists and has a finite value and divergent if the limit doesn’t exist or has infinite value. Cheat sheet for integrals 1. Integrals with trigonometric functions z sinaxdx= 1 a cosax (63) z sin2 axdx= x 2.
Derivative Rules Cheat Sheet
Integrals with trigonometric functions z sinaxdx= 1 a cosax (63) z sin2 axdx= x 2 sin2ax 4a (64) z sinn axdx= 1 a cosax 2f 1 1 2; Integral is called convergent if the limit exists and has a finite value and divergent if the limit doesn’t exist or has infinite value. ( ) 𝑥=𝑥⋅ ( ) ∫taking a constant.
Page 1 of 2 Some Important Rules Of Differential & Integral Calculus
( ) 𝑥=𝑥⋅ ( ) ∫taking a constant out: Cheat sheet for integrals 1. Integrals with trigonometric functions z sinaxdx= 1 a cosax (63) z sin2 axdx= x 2 sin2ax 4a (64) z sinn axdx= 1 a cosax 2f 1 1 2; Integral is called convergent if the limit exists and has a finite value and divergent if the limit.
Integral cheat sheet Docsity
Integrals with trigonometric functions z sinaxdx= 1 a cosax (63) z sin2 axdx= x 2 sin2ax 4a (64) z sinn axdx= 1 a cosax 2f 1 1 2; ⋅ (𝑥 ) 𝑥= ⋅∫ 𝑥 𝑥 ∫sum/difference. ( ) 𝑥=𝑥⋅ ( ) ∫taking a constant out: Integral of a constant \int f\left(a\right)dx=x\cdot f\left(a\right) take the constant out \int a\cdot f\left(x\right)dx=a\cdot \int.
Integral Of A Constant \Int F\Left(A\Right)Dx=X\Cdot F\Left(A\Right) Take The Constant Out \Int A\Cdot F\Left(X\Right)Dx=A\Cdot \Int F\Left(X\Right)Dx.
Integrals with trigonometric functions z sinaxdx= 1 a cosax (63) z sin2 axdx= x 2 sin2ax 4a (64) z sinn axdx= 1 a cosax 2f 1 1 2; Cheat sheet for integrals 1. ′= −∫ ′ ∫integral of a constant: ( ) 𝑥=𝑥⋅ ( ) ∫taking a constant out:
Integral Is Called Convergent If The Limit Exists And Has A Finite Value And Divergent If The Limit Doesn’t Exist Or Has Infinite Value.
⋅ (𝑥 ) 𝑥= ⋅∫ 𝑥 𝑥 ∫sum/difference.