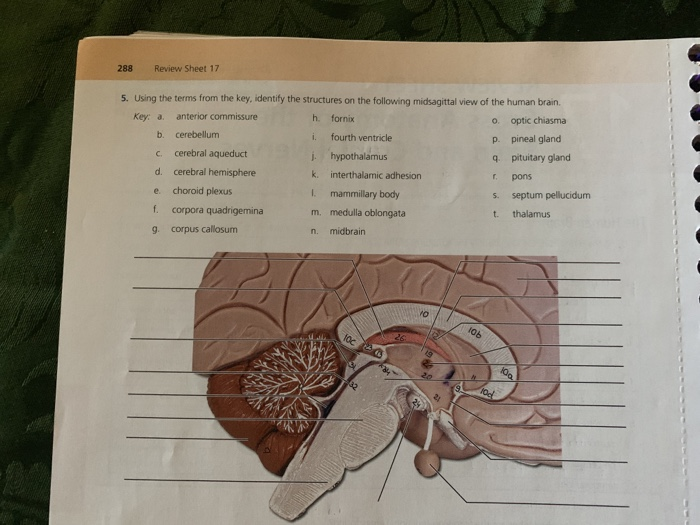
Gross Anatomy Of The Brain And Cranial Nerves Review Sheet
Gross Anatomy Of The Brain And Cranial Nerves Review Sheet - A dural fold separating the cerebrum from the. Embryologically, the brain arises from the rostral end of tubelike structure that quickly becomes divided into three major regions. Cerebral hemispheres, cerebellum, diencephalon a(n) _________ is an elevated. Groups of structures that develop from the embryonic brain are listed below. Designate the embryonic origin of each group. Learn at your own pace. Which of the following structures are not part of the brain stem? A dural fold that attaches the cerebrum to the crista galli of th e skull 8. 278 review sheet 14 7.
Which of the following structures are not part of the brain stem? Cerebral hemispheres, cerebellum, diencephalon a(n) _________ is an elevated. Embryologically, the brain arises from the rostral end of tubelike structure that quickly becomes divided into three major regions. Groups of structures that develop from the embryonic brain are listed below. Learn at your own pace. A dural fold that attaches the cerebrum to the crista galli of th e skull 8. A dural fold separating the cerebrum from the. 278 review sheet 14 7. Designate the embryonic origin of each group.
Designate the embryonic origin of each group. A dural fold that attaches the cerebrum to the crista galli of th e skull 8. Which of the following structures are not part of the brain stem? Embryologically, the brain arises from the rostral end of tubelike structure that quickly becomes divided into three major regions. Cerebral hemispheres, cerebellum, diencephalon a(n) _________ is an elevated. Learn at your own pace. 278 review sheet 14 7. A dural fold separating the cerebrum from the. Groups of structures that develop from the embryonic brain are listed below.
Gross Anatomy Of Brain And Cranial Nerves
Embryologically, the brain arises from the rostral end of tubelike structure that quickly becomes divided into three major regions. Groups of structures that develop from the embryonic brain are listed below. Designate the embryonic origin of each group. A dural fold that attaches the cerebrum to the crista galli of th e skull 8. Learn at your own pace.
Facial Nerve Anatomy, Cranial Nerves Anatomy, Cranial Nerves Mnemonic
Which of the following structures are not part of the brain stem? Designate the embryonic origin of each group. Learn at your own pace. A dural fold that attaches the cerebrum to the crista galli of th e skull 8. Embryologically, the brain arises from the rostral end of tubelike structure that quickly becomes divided into three major regions.
Cranial Nerves Nursing school notes, Medical school essentials
Cerebral hemispheres, cerebellum, diencephalon a(n) _________ is an elevated. Designate the embryonic origin of each group. Groups of structures that develop from the embryonic brain are listed below. Which of the following structures are not part of the brain stem? Embryologically, the brain arises from the rostral end of tubelike structure that quickly becomes divided into three major regions.
Review Sheet Gross Anatomy Of The Brain And Cranial Nerves Anatomical
278 review sheet 14 7. Learn at your own pace. Embryologically, the brain arises from the rostral end of tubelike structure that quickly becomes divided into three major regions. A dural fold that attaches the cerebrum to the crista galli of th e skull 8. A dural fold separating the cerebrum from the.
Gross Anatomy of the Brain and Cranial Nerves Studocu
Designate the embryonic origin of each group. 278 review sheet 14 7. Embryologically, the brain arises from the rostral end of tubelike structure that quickly becomes divided into three major regions. Which of the following structures are not part of the brain stem? Groups of structures that develop from the embryonic brain are listed below.
Cranial Nerves (Inferior View of Brain) Diagram Quizlet
A dural fold that attaches the cerebrum to the crista galli of th e skull 8. Designate the embryonic origin of each group. 278 review sheet 14 7. Which of the following structures are not part of the brain stem? Cerebral hemispheres, cerebellum, diencephalon a(n) _________ is an elevated.
Chapter 17 review sheet Human Anatomy and Physiology Page 287 REVIEW
Learn at your own pace. Embryologically, the brain arises from the rostral end of tubelike structure that quickly becomes divided into three major regions. Designate the embryonic origin of each group. 278 review sheet 14 7. Which of the following structures are not part of the brain stem?
Gross anatomy of the Brain and Cranial Nerves Diagram Quizlet
Cerebral hemispheres, cerebellum, diencephalon a(n) _________ is an elevated. 278 review sheet 14 7. A dural fold that attaches the cerebrum to the crista galli of th e skull 8. A dural fold separating the cerebrum from the. Designate the embryonic origin of each group.
Human Anatomy & Physiology Laboratory Manual Exercise 17 Gross
Groups of structures that develop from the embryonic brain are listed below. A dural fold that attaches the cerebrum to the crista galli of th e skull 8. 278 review sheet 14 7. Cerebral hemispheres, cerebellum, diencephalon a(n) _________ is an elevated. Embryologically, the brain arises from the rostral end of tubelike structure that quickly becomes divided into three major.
Which Of The Following Structures Are Not Part Of The Brain Stem?
Learn at your own pace. Cerebral hemispheres, cerebellum, diencephalon a(n) _________ is an elevated. Groups of structures that develop from the embryonic brain are listed below. Designate the embryonic origin of each group.
A Dural Fold That Attaches The Cerebrum To The Crista Galli Of Th E Skull 8.
A dural fold separating the cerebrum from the. Embryologically, the brain arises from the rostral end of tubelike structure that quickly becomes divided into three major regions. 278 review sheet 14 7.