Cognitive Avoidance
Cognitive Avoidance - There are two types of avoidance — cognitive and behavioral. Avoidance is a strategy we use to escape a stressful experience. Avoidance is typically considered a maladaptive behavioral response to excessive fear and anxiety, leading to the maintenance of anxiety. Cognitive avoidance can lead to. This occurs when individuals try to avoid distressing thoughts or memories.
This occurs when individuals try to avoid distressing thoughts or memories. There are two types of avoidance — cognitive and behavioral. Avoidance is typically considered a maladaptive behavioral response to excessive fear and anxiety, leading to the maintenance of anxiety. Avoidance is a strategy we use to escape a stressful experience. Cognitive avoidance can lead to.
This occurs when individuals try to avoid distressing thoughts or memories. Avoidance is typically considered a maladaptive behavioral response to excessive fear and anxiety, leading to the maintenance of anxiety. There are two types of avoidance — cognitive and behavioral. Avoidance is a strategy we use to escape a stressful experience. Cognitive avoidance can lead to.
Cognitive Behavioural Avoidance Scale
Avoidance is a strategy we use to escape a stressful experience. Avoidance is typically considered a maladaptive behavioral response to excessive fear and anxiety, leading to the maintenance of anxiety. There are two types of avoidance — cognitive and behavioral. This occurs when individuals try to avoid distressing thoughts or memories. Cognitive avoidance can lead to.
Brain Sciences Free FullText Cognitive Avoidance Is Associated
There are two types of avoidance — cognitive and behavioral. Avoidance is a strategy we use to escape a stressful experience. This occurs when individuals try to avoid distressing thoughts or memories. Avoidance is typically considered a maladaptive behavioral response to excessive fear and anxiety, leading to the maintenance of anxiety. Cognitive avoidance can lead to.
Brain Sciences Free FullText Cognitive Avoidance Is Associated
Avoidance is a strategy we use to escape a stressful experience. There are two types of avoidance — cognitive and behavioral. This occurs when individuals try to avoid distressing thoughts or memories. Avoidance is typically considered a maladaptive behavioral response to excessive fear and anxiety, leading to the maintenance of anxiety. Cognitive avoidance can lead to.
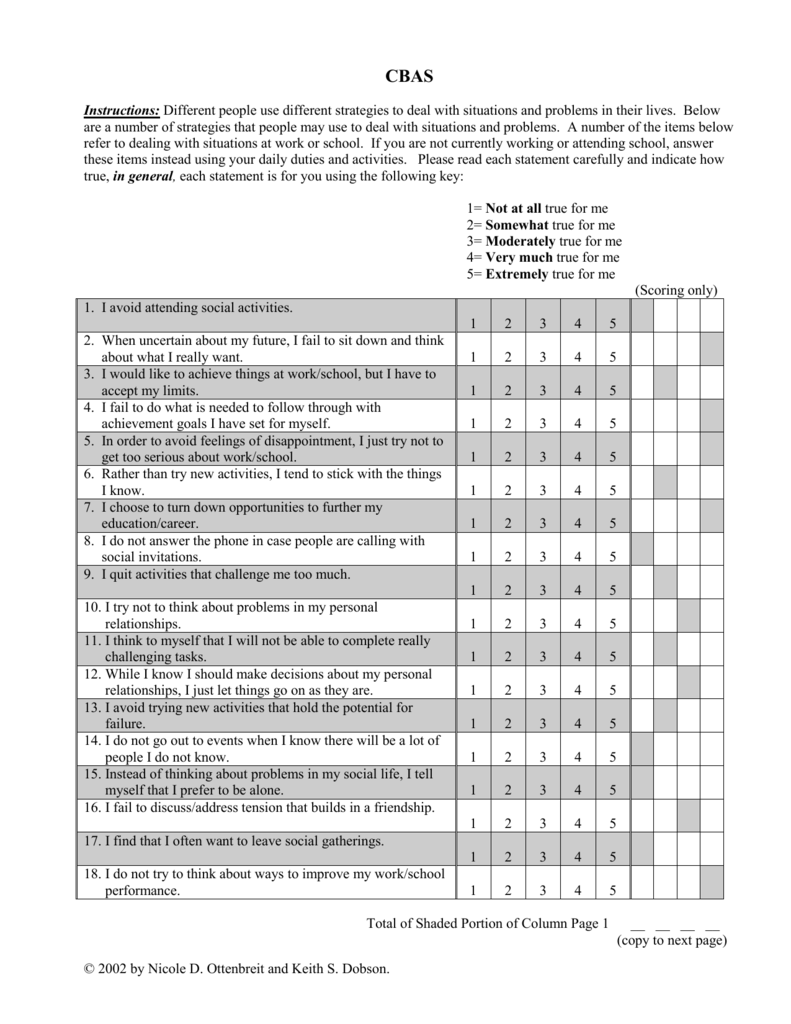
Table 1 from Cognitive Avoidance Questionnaire Factor structure and
Cognitive avoidance can lead to. There are two types of avoidance — cognitive and behavioral. This occurs when individuals try to avoid distressing thoughts or memories. Avoidance is typically considered a maladaptive behavioral response to excessive fear and anxiety, leading to the maintenance of anxiety. Avoidance is a strategy we use to escape a stressful experience.
Schematic overview of the cognitivebehavioral fearavoidance model
Avoidance is a strategy we use to escape a stressful experience. Cognitive avoidance can lead to. Avoidance is typically considered a maladaptive behavioral response to excessive fear and anxiety, leading to the maintenance of anxiety. There are two types of avoidance — cognitive and behavioral. This occurs when individuals try to avoid distressing thoughts or memories.
Table 2 from Cognitive Avoidance Questionnaire Factor structure and
Avoidance is a strategy we use to escape a stressful experience. This occurs when individuals try to avoid distressing thoughts or memories. Cognitive avoidance can lead to. Avoidance is typically considered a maladaptive behavioral response to excessive fear and anxiety, leading to the maintenance of anxiety. There are two types of avoidance — cognitive and behavioral.
Cognitive avoidance for males and females over time. Download
Avoidance is typically considered a maladaptive behavioral response to excessive fear and anxiety, leading to the maintenance of anxiety. Cognitive avoidance can lead to. This occurs when individuals try to avoid distressing thoughts or memories. There are two types of avoidance — cognitive and behavioral. Avoidance is a strategy we use to escape a stressful experience.
Why Mental Mistakes Get Made 18 Cognitive Bias Examples The Big Picture
This occurs when individuals try to avoid distressing thoughts or memories. Avoidance is a strategy we use to escape a stressful experience. There are two types of avoidance — cognitive and behavioral. Cognitive avoidance can lead to. Avoidance is typically considered a maladaptive behavioral response to excessive fear and anxiety, leading to the maintenance of anxiety.
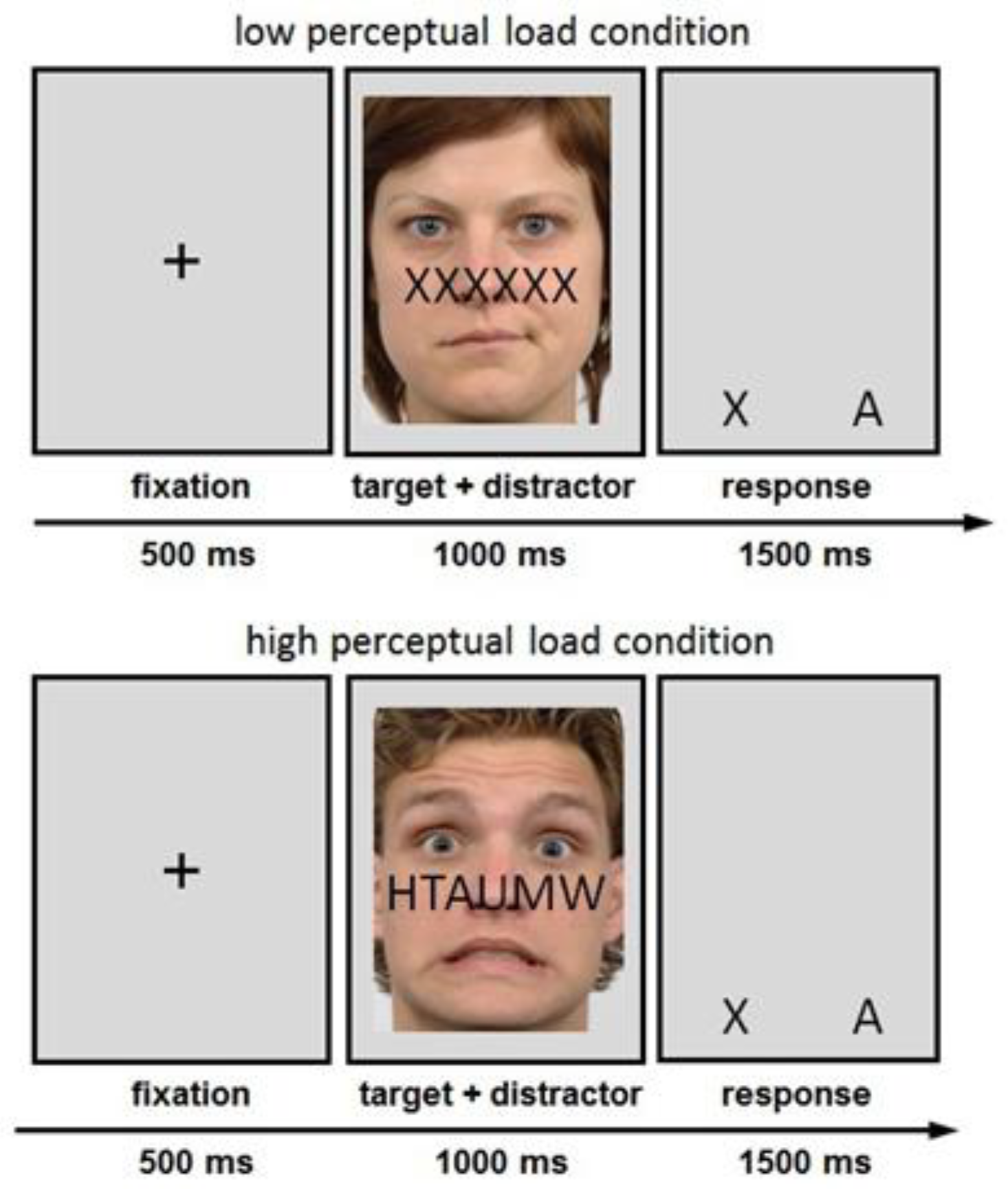
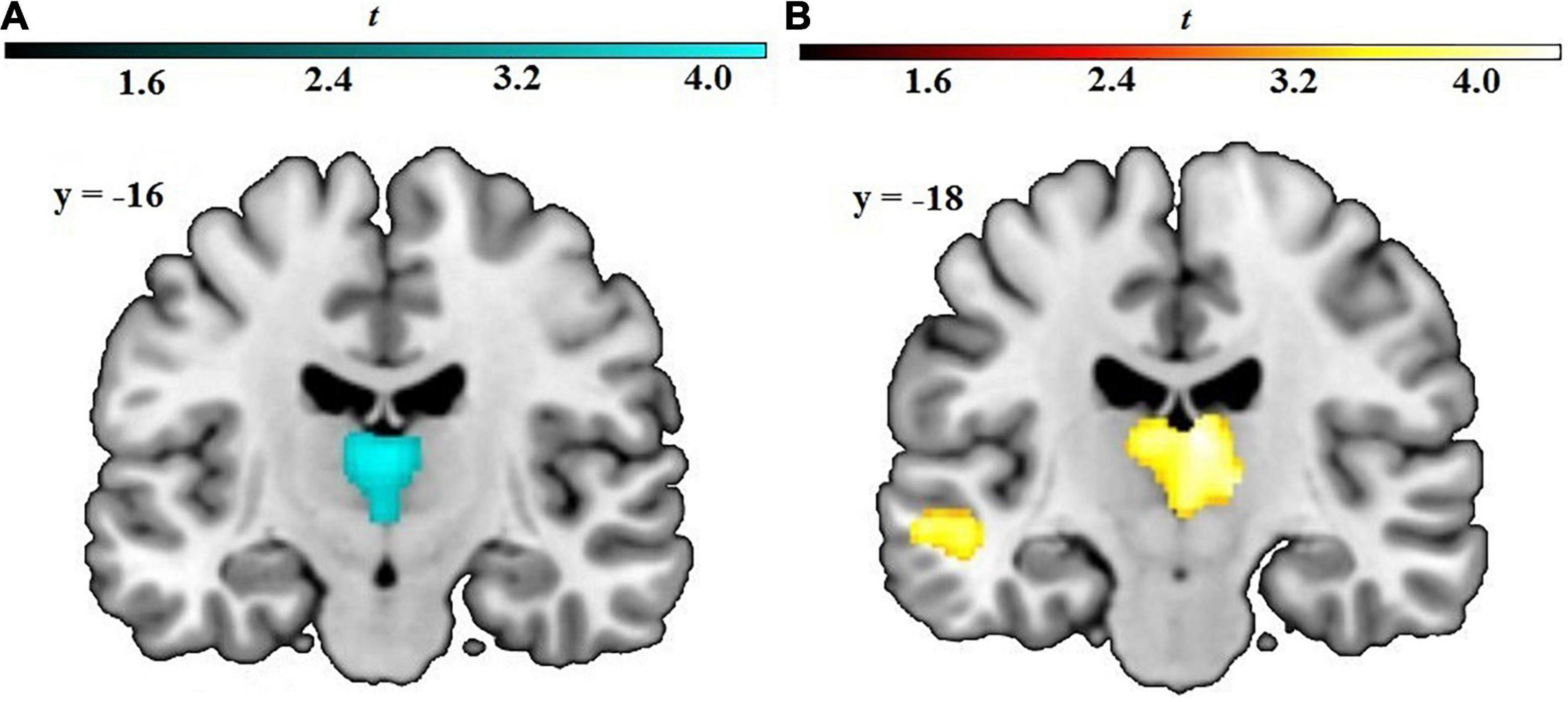
Frontiers Coping With Anxiety Brain Structural Correlates of
There are two types of avoidance — cognitive and behavioral. Cognitive avoidance can lead to. Avoidance is typically considered a maladaptive behavioral response to excessive fear and anxiety, leading to the maintenance of anxiety. Avoidance is a strategy we use to escape a stressful experience. This occurs when individuals try to avoid distressing thoughts or memories.
(PDF) Cognitive Avoidance Is Associated with Decreased Brain
There are two types of avoidance — cognitive and behavioral. Avoidance is a strategy we use to escape a stressful experience. Cognitive avoidance can lead to. This occurs when individuals try to avoid distressing thoughts or memories. Avoidance is typically considered a maladaptive behavioral response to excessive fear and anxiety, leading to the maintenance of anxiety.
Avoidance Is A Strategy We Use To Escape A Stressful Experience.
There are two types of avoidance — cognitive and behavioral. This occurs when individuals try to avoid distressing thoughts or memories. Avoidance is typically considered a maladaptive behavioral response to excessive fear and anxiety, leading to the maintenance of anxiety. Cognitive avoidance can lead to.