What Is The Potential Difference Across The 10 ω Resistor
What Is The Potential Difference Across The 10 ω Resistor - Current, potential difference, power and resistance can be calculated to analyse circuits including potential dividers and wheatstone bridges. According to ohm’s law, the potential drop \(v\) across a resistor when a current flows through it is calculated using the equation \(v = ir\), where. According to ohm’s law, the voltage across the resistor is proportional to the current through the r.
Current, potential difference, power and resistance can be calculated to analyse circuits including potential dividers and wheatstone bridges. According to ohm’s law, the potential drop \(v\) across a resistor when a current flows through it is calculated using the equation \(v = ir\), where. According to ohm’s law, the voltage across the resistor is proportional to the current through the r.
According to ohm’s law, the potential drop \(v\) across a resistor when a current flows through it is calculated using the equation \(v = ir\), where. According to ohm’s law, the voltage across the resistor is proportional to the current through the r. Current, potential difference, power and resistance can be calculated to analyse circuits including potential dividers and wheatstone bridges.
How To Calculate Potential Difference Across A Bulb Art & Bussines
According to ohm’s law, the potential drop \(v\) across a resistor when a current flows through it is calculated using the equation \(v = ir\), where. Current, potential difference, power and resistance can be calculated to analyse circuits including potential dividers and wheatstone bridges. According to ohm’s law, the voltage across the resistor is proportional to the current through the.
What Do We Call Resistors Connected In Series In Terms Of Potential
According to ohm’s law, the voltage across the resistor is proportional to the current through the r. Current, potential difference, power and resistance can be calculated to analyse circuits including potential dividers and wheatstone bridges. According to ohm’s law, the potential drop \(v\) across a resistor when a current flows through it is calculated using the equation \(v = ir\),.
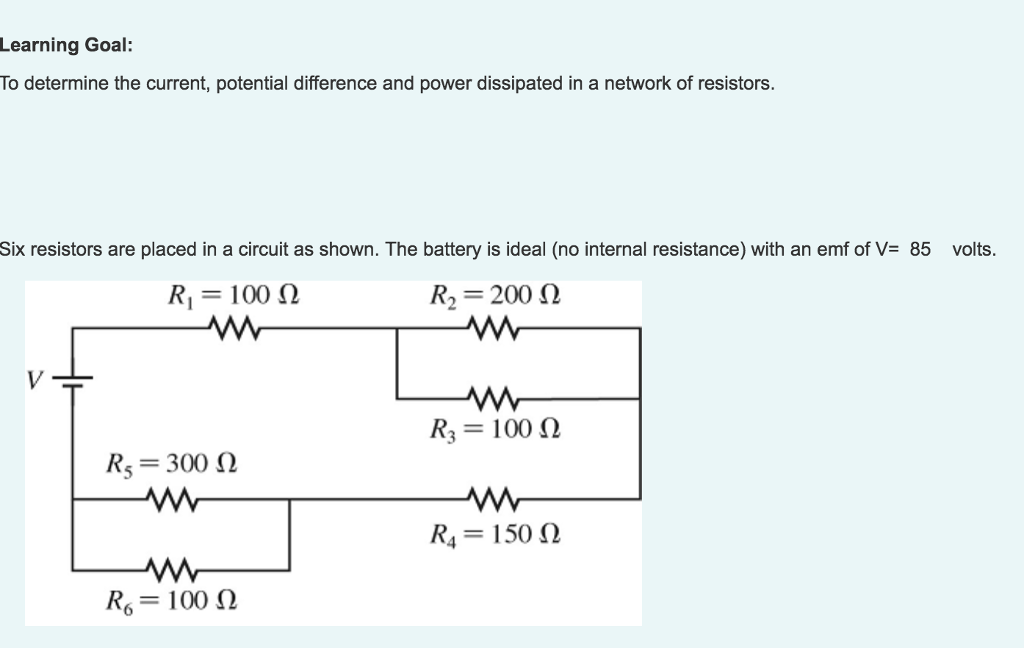
Solved Learning Goal To determine the current, potential
According to ohm’s law, the voltage across the resistor is proportional to the current through the r. Current, potential difference, power and resistance can be calculated to analyse circuits including potential dividers and wheatstone bridges. According to ohm’s law, the potential drop \(v\) across a resistor when a current flows through it is calculated using the equation \(v = ir\),.
Question Video Determining the Potential Difference across a Resistor
According to ohm’s law, the potential drop \(v\) across a resistor when a current flows through it is calculated using the equation \(v = ir\), where. Current, potential difference, power and resistance can be calculated to analyse circuits including potential dividers and wheatstone bridges. According to ohm’s law, the voltage across the resistor is proportional to the current through the.
Solved Find the potential difference across each resistor in
According to ohm’s law, the voltage across the resistor is proportional to the current through the r. According to ohm’s law, the potential drop \(v\) across a resistor when a current flows through it is calculated using the equation \(v = ir\), where. Current, potential difference, power and resistance can be calculated to analyse circuits including potential dividers and wheatstone.
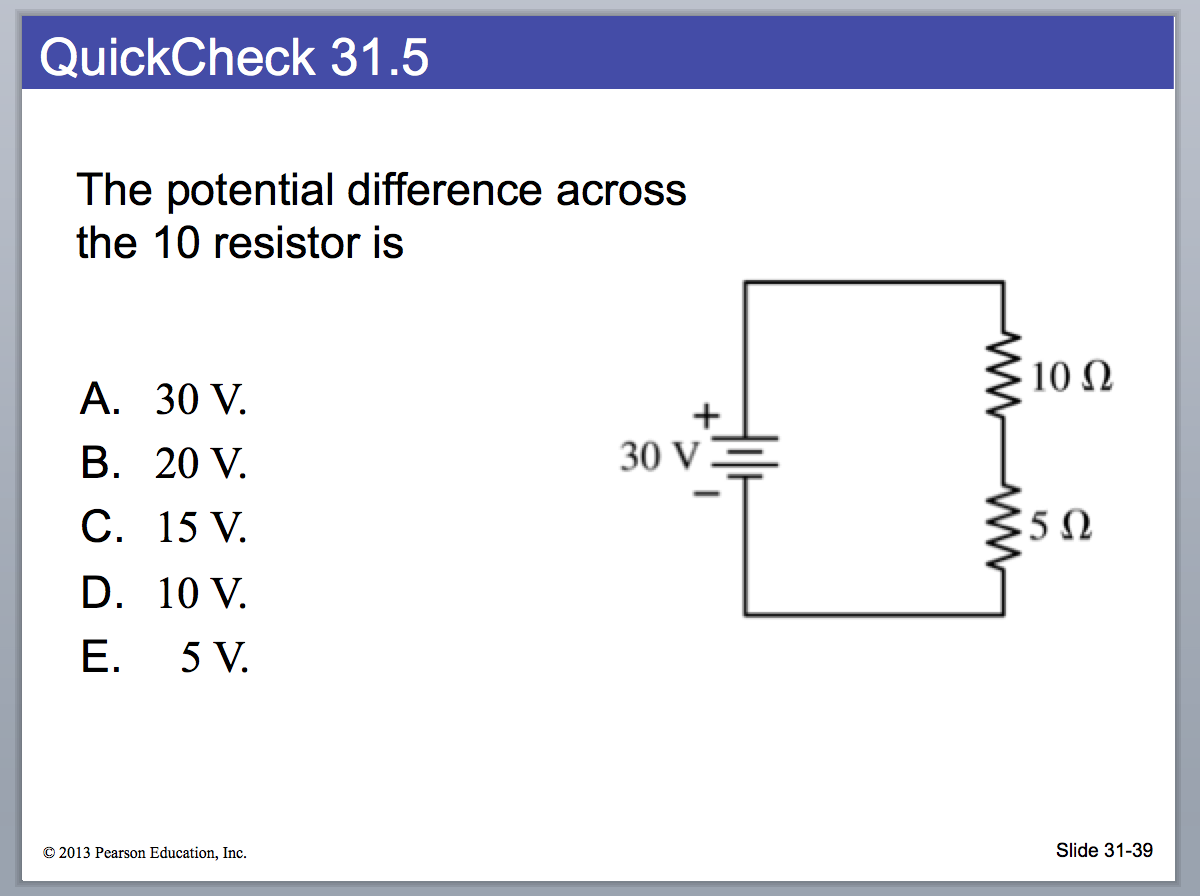
Solved The potential difference across the 10 resistor is A.
According to ohm’s law, the voltage across the resistor is proportional to the current through the r. Current, potential difference, power and resistance can be calculated to analyse circuits including potential dividers and wheatstone bridges. According to ohm’s law, the potential drop \(v\) across a resistor when a current flows through it is calculated using the equation \(v = ir\),.
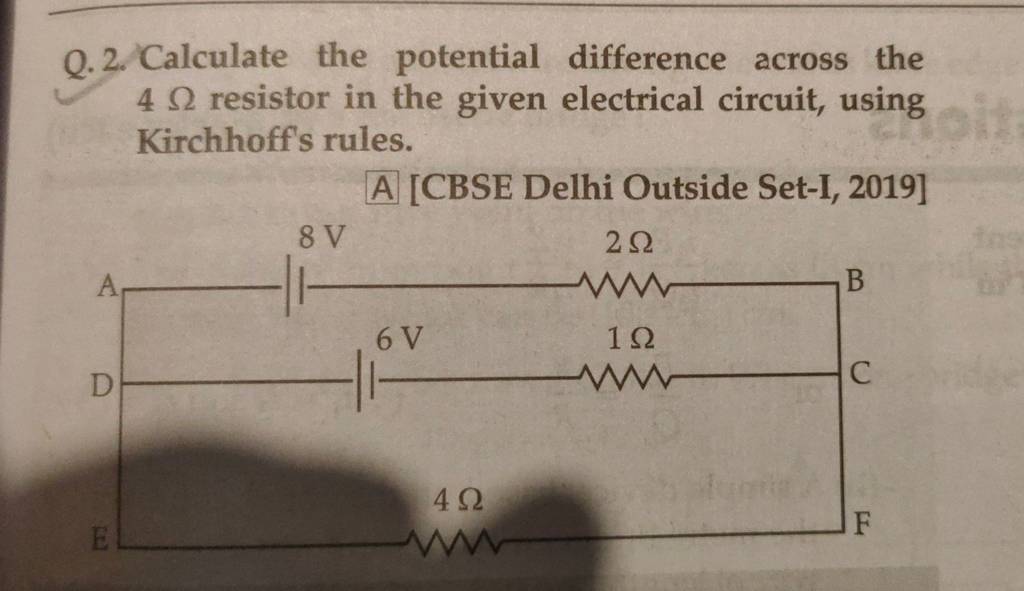
Q.2. Calculate the potential difference across the 4Ω resistor in the giv..
Current, potential difference, power and resistance can be calculated to analyse circuits including potential dividers and wheatstone bridges. According to ohm’s law, the voltage across the resistor is proportional to the current through the r. According to ohm’s law, the potential drop \(v\) across a resistor when a current flows through it is calculated using the equation \(v = ir\),.
(i) the current flowing in the circuit.(ii) the potential difference
Current, potential difference, power and resistance can be calculated to analyse circuits including potential dividers and wheatstone bridges. According to ohm’s law, the voltage across the resistor is proportional to the current through the r. According to ohm’s law, the potential drop \(v\) across a resistor when a current flows through it is calculated using the equation \(v = ir\),.
How To Work Out Potential Difference In A Circuit
According to ohm’s law, the potential drop \(v\) across a resistor when a current flows through it is calculated using the equation \(v = ir\), where. Current, potential difference, power and resistance can be calculated to analyse circuits including potential dividers and wheatstone bridges. According to ohm’s law, the voltage across the resistor is proportional to the current through the.
The potential difference across resistor R3 is Filo
According to ohm’s law, the potential drop \(v\) across a resistor when a current flows through it is calculated using the equation \(v = ir\), where. Current, potential difference, power and resistance can be calculated to analyse circuits including potential dividers and wheatstone bridges. According to ohm’s law, the voltage across the resistor is proportional to the current through the.
According To Ohm’s Law, The Voltage Across The Resistor Is Proportional To The Current Through The R.
Current, potential difference, power and resistance can be calculated to analyse circuits including potential dividers and wheatstone bridges. According to ohm’s law, the potential drop \(v\) across a resistor when a current flows through it is calculated using the equation \(v = ir\), where.